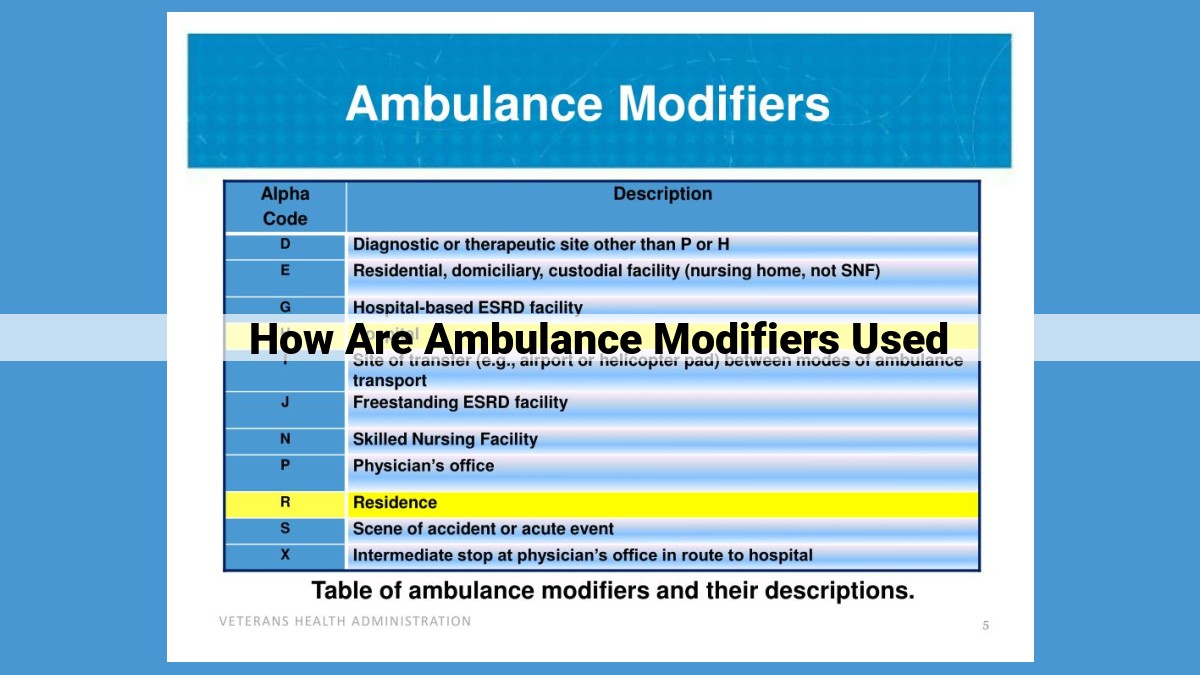
Ambulance modifiers are essential for accurate billing of ambulance services. They differentiate between transport modes (ground, air, water), levels of care (ambulatory, BLS, ALS, critical care), and additional charges (supplies, equipment, staff). By understanding the appropriate modifiers and their application, ambulance providers can ensure accurate reimbursement for the services they provide.
In the fast-paced world of emergency medical services, ambulance billing can be a complex labyrinth. Modifiers are the beacons that guide us through this maze, ensuring accurate reimbursement for the critical services we provide.
Why Modifiers Matter
In ambulance billing, modifiers play a pivotal role in capturing the nuances of our services. They convey specific details about the transport mode, equipment used, and additional charges incurred. By accurately applying modifiers, we can maximize reimbursement and reduce the risk of claim denials.
A Spectrum of Ambulance Services
Ambulance services encompass a wide range, from basic life support to highly specialized critical care transport. Each type of service comes with its own billing considerations, and modifiers help us differentiate them.
-
Ground Transport:
- Ambulatory (non-emergency)
- Basic Life Support (BLS)
- Advanced Life Support (ALS)
-
Air Transport:
- Critical care
- Helicopters
- Airplanes
-
Water Transport:
- Boats
- Ships
Navigating CMS-1500 and UB-04
When submitting ambulance claims, we use either the CMS-1500 or UB-04 claim forms. These forms provide designated fields where modifiers are applied to accurately reflect the details of our transport services.
- CMS-1500: Field 24D “Modifiers”
- UB-04: Field 11 “Revenue Code” (includes modifiers)
Transport Modes and Modifiers in Ambulance Billing
Unveiling the Complexities of Ambulance Transport Services
In the realm of medical emergencies, swift and efficient transportation is paramount. Ambulance services play a vital role in providing emergency medical care and transporting patients to treatment facilities. To ensure accurate billing and reimbursement for these services, a thorough understanding of transport modes and modifiers is essential.
Ground Transport: Variations in Care
Ground transport via ambulance allows for a spectrum of care levels, each with its distinct requirements and billing considerations. Ambulatory transport is utilized for patients who are able to walk or sit upright and do not require extensive medical care during transport. Basic life support (BLS) ambulances provide essential care, including oxygen administration, immobilization, and wound management. For patients requiring more intensive care during transport, advanced life support (ALS) ambulances are deployed, equipped with advanced equipment like defibrillators and ventilators.
Air Transport: Wings for Critical Care
Air transport is employed when speed and access to specialized care are crucial. Critical care air ambulances are fully equipped with advanced life support capabilities, enabling the transport of extremely ill or injured patients over long distances. Helicopters and airplanes are the primary modes of air transport, each offering unique advantages depending on the situation.
Water Transport: Navigating Remote Waters
In coastal or island regions, water transport may be necessary for ambulance services. Boats and ships are utilized to reach patients in remote areas inaccessible by land or air. Billing for water transport involves considerations such as vessel type, distance traveled, and specialized equipment used.
By understanding the nuances of transport modes and modifiers, healthcare providers can ensure accurate billing and maximize reimbursement for ambulance services, ultimately contributing to the provision of timely and high-quality care for patients in need.
Billing Codes for Ambulance Services:
- CMS-1500 and UB-04 claim forms
Understanding Billing Codes for Ambulance Services
When navigating the complexities of ambulance billing, understanding the importance of billing codes is crucial. These codes serve as a universal language, allowing healthcare providers and insurance companies to identify the specific services provided and determine appropriate reimbursement.
Two forms are commonly used for ambulance billing: the CMS-1500 and UB-04.
-
CMS-1500: This form is widely accepted by Medicare and other government-funded insurance programs. It includes fields for patient information, medical services rendered, and charges.
-
UB-04: This form is typically used by private insurers and healthcare facilities. It provides more comprehensive information compared to the CMS-1500, including fields for patient demographics, diagnosis, and treatment codes.
Effective Utilization of Billing Codes
Using accurate billing codes ensures proper reimbursement and avoids potential delays or denials. Ambulance services should carefully review the patient’s condition, the services provided, and the appropriate billing codes.
For example, if an ambulance responds to a call for a patient experiencing chest pain, the following codes may be used:
- G0290: Basic life support, air transport
- A0375: Transportation distance (per mile)
Importance of Specificity
Using specific billing codes is essential as they provide detailed information about the services rendered. This specificity helps insurers understand the level of care provided and make informed decisions regarding reimbursement.
By understanding and accurately using billing codes, ambulance services can streamline their billing process, improve reimbursement, and ensure that patients receive the appropriate coverage for their services.
Mileage Modifiers in Ambulance Billing: Accurately Reimbursing for Distance and Round Trips
Accurate billing is crucial for ambulance providers to ensure fair reimbursement and maintain financial stability. Mileage modifiers play a significant role in ambulance billing, compensating for the distance traveled and the cost of round trips.
The per mile modifier is used to calculate distance-based reimbursement. This modifier is applied to the mileage rate set by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). By multiplying the mileage rate by the distance traveled, ambulance providers can determine the reimbursement for transporting patients.
In addition to the per mile modifier, the round trip modifier allows ambulance providers to charge for both the outbound and return legs of a transport. This modifier is particularly important when the return trip is not immediately after the outbound trip, as it compensates for the additional time and resources required.
Understanding and correctly applying these mileage modifiers are essential for accurate billing. Ambulance providers should carefully document the distance traveled and any round trips to ensure that they receive appropriate reimbursement.
Example:
An ambulance transports a patient from their home to a hospital 20 miles away. The mileage rate set by CMS is $1.50 per mile. Using the per mile modifier, the ambulance provider would be reimbursed $200 (20 miles x $1.50 per mile).
If the ambulance then transports the patient back home, the round trip modifier would be applied. The ambulance provider would then be reimbursed an additional $200 (20 miles x $1.50 per mile x 2).
By utilizing these mileage modifiers, ambulance providers can ensure that they are fairly compensated for the distance traveled and the round trips they perform, contributing to their financial viability and the provision of essential emergency medical services.
Additional Charges and Modifiers: Enhancing Ambulance Billing Accuracy
Beyond the core transport services, ambulance providers may incur additional costs for supplies, equipment, and staff that enhance patient care. Understanding and applying appropriate modifiers for these expenses ensures accurate billing and reimbursement.
Supplies Modifier
The supplies modifier is used to bill for medical supplies utilized during transport. This may include items such as bandages, dressings, medications, and oxygen tanks. Accurately documenting the supplies used and applying the appropriate modifier helps ensure proper reimbursement.
Equipment Modifier
When specialized equipment is necessary for patient care, the equipment modifier is utilized. This may include stretchers, monitors, ventilators, or defibrillators. The modifier specifies the type of equipment used, ensuring reimbursement for these vital tools.
Staff Modifier
In cases where additional medical professionals are required for the safe transport of a patient, the staff modifier is applied. This may include paramedics, nurses, or physicians who provide advanced medical care during transport. By accurately documenting the additional staff involved, ambulance providers optimize reimbursement for these essential services.
By effectively using these additional modifiers, ambulance providers can ensure comprehensive and accurate billing. This allows for fair reimbursement for the full range of services provided, ultimately ensuring the financial viability of ambulance services and the continued provision of quality patient care.
Effective Use of Ambulance Modifiers: Impact on Billing and Reimbursement
Ambulance modifiers are essential tools in the billing process, providing crucial information that ensures accurate reimbursement for ambulance services. By understanding the impact of modifiers on billing accuracy and reimbursement, ambulance providers can optimize their claims and maximize revenue.
How Modifiers Impact Billing Accuracy
Modifiers play a vital role in providing detailed information about the services rendered during ambulance transport. They specify the type of transport, equipment used, distance traveled, and additional charges incurred. This precise information ensures that claims are processed correctly, preventing denials or delays in reimbursement.
Combining Modifiers for Comprehensive Billing
Combining modifiers effectively is key to capturing the full range of services provided during an ambulance transport. For instance, if an ambulance transports a patient via ground with advanced life support and utilizes specialized equipment, the following modifiers could be combined:
- G0464: Ambulatory transport
- A0453: Advanced life support
- E0476: Specialized equipment
By combining these modifiers, the ambulance provider accurately reflects the services rendered, ensuring appropriate reimbursement.
Maximizing Reimbursement through Effective Modifier Usage
By utilizing modifiers judiciously, ambulance providers can increase the accuracy of their claims and maximize reimbursement. Submitting complete and accurate claims reduces the risk of denials, improves cash flow, and ensures that ambulance services are compensated fairly for the critical care they provide.
Understanding how ambulance modifiers impact billing and reimbursement empowers providers to optimize their revenue cycle management. By effectively combining modifiers, they can accurately represent the services rendered and ensure that their claims are processed efficiently, leading to timely and optimal reimbursement.