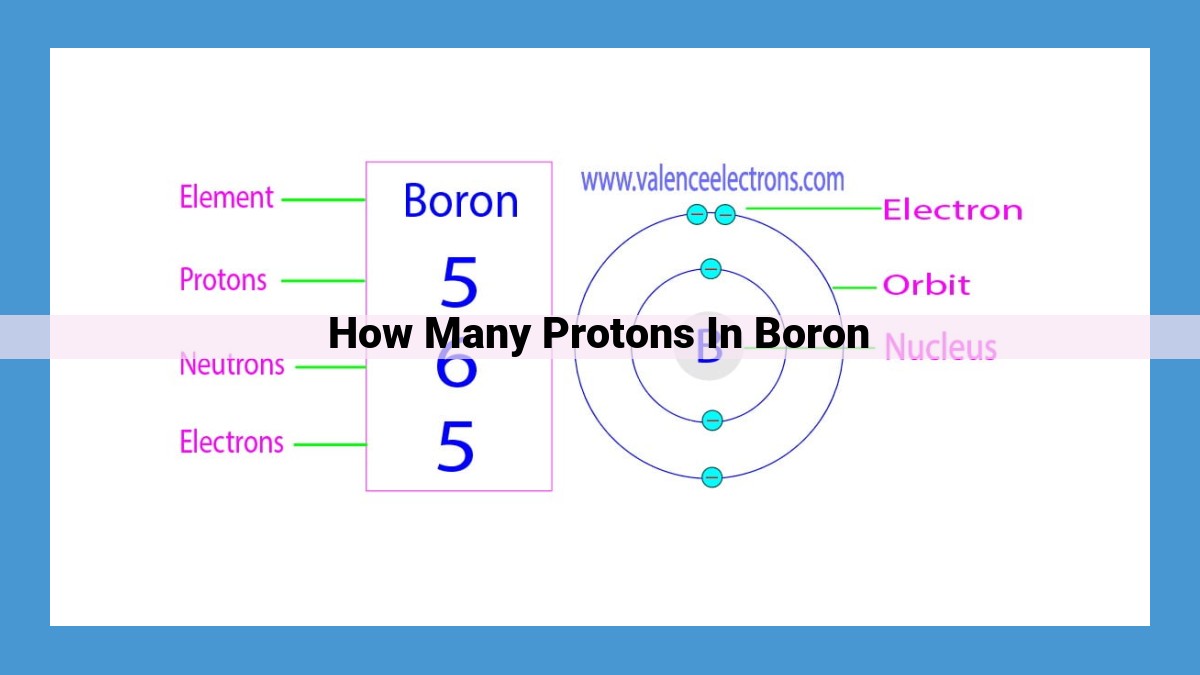
The atomic number of boron is 5, indicating that each boron atom has 5 protons in its nucleus. Protons carry a positive charge and are fundamental building blocks of atoms. Boron is a metalloid element with properties of both metals and nonmetals. The atomic number of an element uniquely identifies it and determines the number of protons in its nucleus.
Atomic Number: The Key to Understanding Proton Count
In the intricate world of chemistry, the atomic number stands as a crucial concept that unravels the secrets of an element’s identity. Atomic number encapsulates the number of protons lurking within an element’s nucleus, the central core of an atom. These protons, imbued with a positive electric charge, play a pivotal role as the fundamental building blocks of atoms.
Imagine an element like boron, with its atomic number of 5. This value reveals that each boron atom harbors five protons within its nucleus. These protons determine boron’s proton number, an alternative term that mirrors atomic number’s significance.
An element’s atomic number serves as a unique fingerprint, distinguishing it from all other elements. Boron, for example, stands out as the element with uniquely five protons. This atomic signature governs the element’s properties, shaping its chemical behavior and physical characteristics.
Boron’s atomic number places it among the metalloids, a fascinating class of elements that exhibit a blend of metallic and nonmetallic properties. Boron’s intriguing nature arises from its ability to both conduct electricity like a metal and form covalent bonds like a nonmetal.
Understanding atomic number empowers us to unravel the secrets of the elements and their behavior. As the key to proton count, it unlocks the mysteries of the microscopic world, enabling us to comprehend the fundamental nature of matter and its intricate interactions.
Proton Number: Another Name for Atomic Number
In the realm of chemistry, the term “proton number” often surfaces alongside its more familiar counterpart, “atomic number.” Both terms share a profound significance, referring to the identical concept: the number of protons residing within an element’s nucleus.
In the heart of every atom lies a nucleus, a densely packed core that houses protons and neutrons. Protons, positively charged particles, are the fundamental building blocks of atoms, defining their elemental identity. The atomic number, or proton number, serves as a unique identifier for each element, as it dictates the number of protons in its nucleus.
For instance, the element boron, with an atomic number of 5, possesses 5 protons in its nucleus. This pivotal number distinguishes boron from all other elements, making it an element with a distinct and immutable identity.
Understanding the proton number is essential for comprehending the chemical behaviors and properties of elements. When atoms interact, forming molecules and compounds, their proton numbers play a decisive role in determining their chemical bonding and reactivity.
Hence, the terms “atomic number” and “proton number” are interchangeable, both denoting the fundamental quantity that defines the essence of every element and guides its chemical destiny.
Boron: An Element with 5 Protons
- State that boron has an atomic number of 5.
- Describe boron’s properties as a metalloid with traits of both metals and nonmetals.
Boron: An Intriguing Metalloid with Five Protons
In the fascinating realm of chemistry, elements reign supreme. These fundamental building blocks of matter cannot be broken down any further chemically, each possessing a unique atomic number. This number, akin to a fingerprint, identifies the element and determines its distinctive properties.
One such element is boron, a captivating metalloid that resides at atomic number 5. Its atomic nucleus harbors five protons, positively charged particles that play a pivotal role in defining boron’s character. These protons, along with electrically neutral neutrons, form the core of every boron atom, while electrons dance around the nucleus in a dynamic ballet.
Boron’s atomic number also coincides with its proton number, a term frequently used interchangeably. Both terms essentially convey the number of protons within the nucleus, providing a key indicator of boron’s identity.
This metalloid possesses a captivating duality, exhibiting traits of both metals and nonmetals. Its luster, malleability, and electrical conductivity hint at metallic qualities. However, its ability to form covalent bonds, a characteristic of nonmetals, sets it apart from its purely metallic counterparts. This unique blend of properties makes boron a versatile material used in a wide spectrum of applications, from glassmaking to fertilizers.
Boron’s distinctive nature stems from its five protons, a fundamental aspect that sets it apart from other elements. It is this atomic fingerprint that governs boron’s reactivity, bonding behavior, and ultimately, its role in the grand tapestry of matter.
Element: The Building Blocks of Matter
In the vast tapestry of the universe, matter exists in an intricate dance of elements, each with its unique identity and properties. An element, at its core, is a substance that cannot be further simplified chemically. It stands as a fundamental building block, indivisible by ordinary means.
Central to each element’s identity lies its atomic number, a numerical value that governs the number of protons within its nucleus. Protons, the positively charged inhabitants of the atom’s heart, are the defining factor that sets one element apart from another.
Imagine a chemical symphony, where each element plays a distinct note. The atomic number serves as the conductor of this symphony, determining the element’s place on the periodic table and its characteristic behaviors. It is the key that unlocks the element’s chemical personality, shaping its reactivity and defining its role in the natural world.