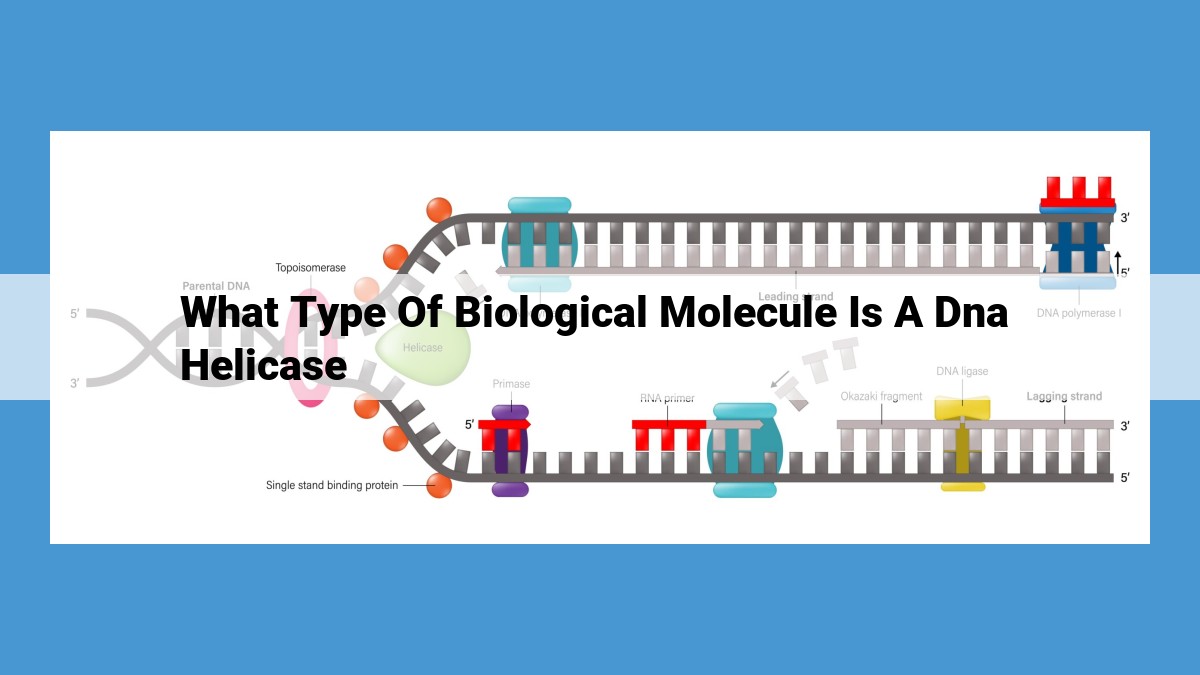
DNA helicase is a protein enzyme that plays a crucial role in the replication of DNA. It unwinds the double helix of DNA, allowing other enzymes to access the genetic material and make copies of it. DNA helicase is a type of helicase, which is a protein enzyme that unwinds the double helix of nucleic acids. Enzymes are biological molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions and DNA helicase is a catalytic enzyme that helps unwind the DNA double helix.
- Define DNA helicase and its role in the process of replication.
Unveiling the Secrets of DNA Helicase: The Molecular Maestro of DNA Replication
In the realm of molecular biology, DNA helicase reigns supreme as the maestro of DNA replication, a process crucial for the perpetuation of life. DNA helicase, an enzyme with an essential role, possesses the remarkable ability to unwind the double helix of DNA, preparing it for replication.
Imagine a tightly coiled ladder representing the double helix of DNA. The rungs of this ladder symbolize the base pairs that hold the DNA strands together. DNA helicase acts as the key, unlocking these rungs one by one, allowing the DNA strands to separate. Without the tireless work of DNA helicase, DNA replication would grind to a halt, rendering cell division and growth impossible.
Biological Molecules: The Building Blocks of Life
The human body is an intricate symphony of biological molecules, each playing a vital role in our very existence. These molecules fall into four main categories: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrates, the body’s primary source of energy, serve as fuel for our cells. They come in two forms: simple (sugars like glucose) and complex (starches like cellulose).
Proteins are essential for structure and function. They make up everything from muscles and enzymes to hormones and antibodies. Proteins are long chains of amino acids, each with a specific role in the body.
Lipids, or fats, come in many forms, including triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol. They provide energy storage, insulate and cushion our organs, and support hormone production.
Nucleic acids, the blueprints of our cells, hold the genetic information that dictates our traits. They come in two forms: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
DNA helicase: A Protein Molecule
Amidst this symphony of molecules, DNA helicase stands out as a protein molecule with a pivotal role in DNA replication. This enzyme plays a crucial part in the process of duplicating our genetic material during cell division.
Unraveling the DNA Puzzle
DNA is a double helix, a twisted ladder-like structure. Before it can be replicated, the two strands of DNA must be separated. This is where DNA helicase comes in. This enzyme acts like a molecular crowbar, unwinding the DNA helix and creating a replication fork. This allows DNA polymerases, other enzymes, to access the DNA template and synthesize new complementary strands.
The Dance of Replication
DNA replication is a complex and precise process, and DNA helicase is an indispensable player. As a protein enzyme, it catalyzes the unwinding of the DNA double helix, a critical step in the replication cycle.
Without DNA helicase, our cells would be unable to duplicate their genetic material, leading to genetic abnormalities and potentially life-threatening consequences. Thus, this remarkable protein enzyme plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of our genetic code and ensuring the continuity of life.
Helicase: The Unsung Hero of DNA Replication
In the intricate tapestry of life’s processes, there lies a remarkable molecule known as DNA helicase. This unassuming yet indispensable enzyme plays a pivotal role in the very foundation of our genetic inheritance: the replication of DNA.
Imagine DNA as a twisted ladder, its sides held together by a tightly woven network of nucleotide base pairs. For this ladder to be copied, the delicate strands must be unwound, creating a “replication bubble.” Enter helicase.
Helicase, a member of the helicase enzyme family, is a molecular machine that possesses the extraordinary ability to break the hydrogen bonds holding the DNA strands together. It deftly pries these strands apart, creating an opening for other enzymes to come into play and synthesize new DNA strands complementary to the originals.
Without DNA helicase, the unwinding of DNA would be akin to trying to untangle a Gordian knot with bare hands. The replication process would grind to a halt, preventing cells from dividing and ultimately leading to catastrophic consequences for all living organisms.
So, next time you hear the term “DNA replication” , remember the unsung hero behind the scenes: helicase. Its tireless unwinding action ensures that the blueprints of life are faithfully transmitted from generation to generation, allowing the tapestry of life to continue its vibrant dance.
Enzymes and DNA Helicase: The Catalytic Unwinders of DNA
In the complex world of our cells, countless chemical reactions take place, facilitated by specialized molecules called enzymes. Among these enzymes is DNA helicase, a protein with a unique ability to unzip the tightly coiled double helix structure of DNA, making it accessible for replication.
Enzymes: The Masters of Reactions
Enzymes are biological catalysts, meaning they speed up chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. They act like molecular matchmakers, bringing specific reactants together in just the right way to facilitate their interaction. This catalytic activity is essential for countless processes within our cells, including DNA replication.
DNA Helicase: The Unwinder of DNA’s Helix
DNA helicase is a specific type of enzyme that plays a crucial role in DNA replication. Its mission is to unzip the tightly wound double helix of DNA into two single strands. This unwinding is necessary for DNA polymerases, the enzymes that synthesize new DNA strands, to gain access to the DNA template and add complementary nucleotides.
DNA helicase achieves this unwinding by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the base pairs together, essentially unzipping the double helix. This process requires energy, which DNA helicase obtains from the hydrolysis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
The Dynamic Duo: Enzymes and DNA Helicase
The relationship between enzymes and DNA helicase is a symbiotic one. DNA helicase relies on its enzymatic properties to unwind DNA, while the catalytic activity of DNA helicase is essential for the overall process of DNA replication. Without DNA helicase, the double helix would remain tightly wound, preventing the replication machinery from accessing the DNA template and synthesizing new strands.
DNA helicase, a protein enzyme, plays a critical role in DNA replication by unwinding the DNA double helix. Its catalytic activity is essential for making the DNA template accessible to DNA polymerases, allowing them to synthesize new DNA strands. This process is crucial for the maintenance and transmission of genetic information, ensuring the seamless division and duplication of cells.