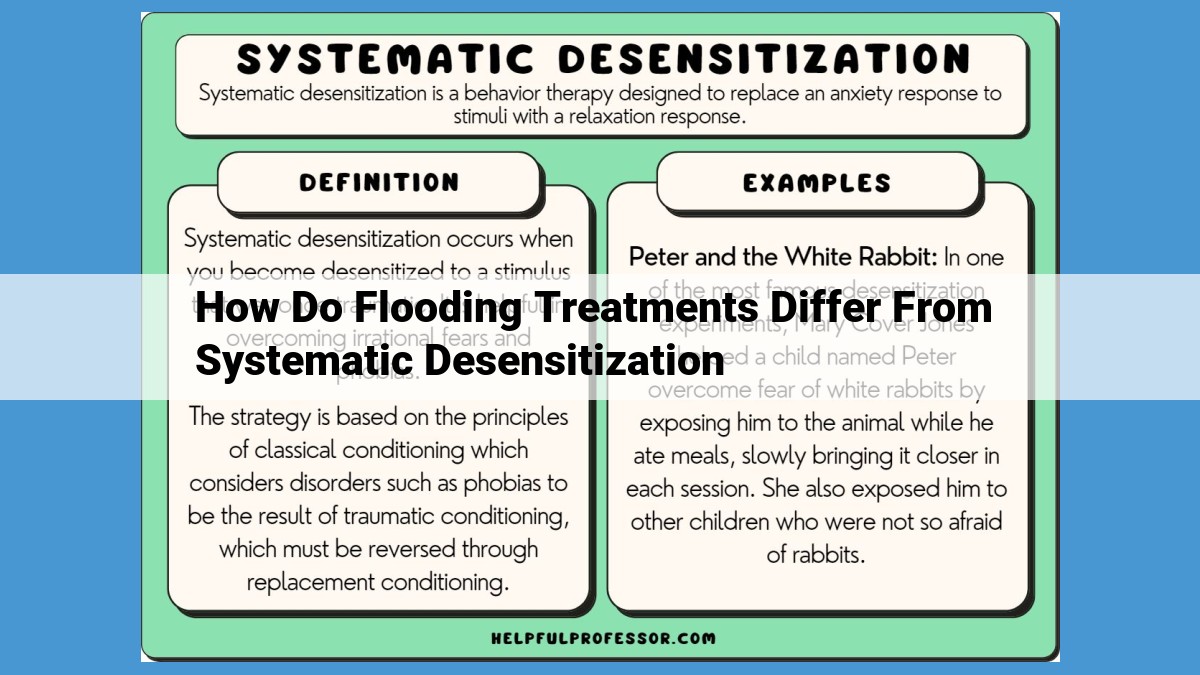
Flooding and systematic desensitization differ in their treatment approaches. Flooding involves prolonged exposure to feared stimuli without escape, which aims to rapidly extinguish fear responses through habituation. Systematic desensitization gradually exposes individuals to anxiety-provoking stimuli while teaching coping skills, fostering cognitive involvement in fear reduction. Flooding sessions elicit high anxiety, while systematic desensitization gradually increases anxiety levels. Relapse prevention strategies may vary, with systematic desensitization emphasizing homework assignments and booster sessions. Both treatments are effective for specific anxiety disorders, with flooding often used for phobias and systematic desensitization for more complex anxiety conditions. Safety concerns may arise during flooding, requiring careful assessment and planning for individuals with severe anxiety or comorbid conditions.
Goals of Flooding and Systematic Desensitization:
- Explain the different objectives of each treatment in eliminating fear responses.
Goals of Flooding and Systematic Desensitization: Unveiling the Dissimilarities
In the realm of psychology, two effective treatments for eliminating fear responses stand out: flooding and systematic desensitization. While both therapies share the common goal of reducing anxiety, they differ significantly in their approaches and objectives.
Flooding: A Confrontational Encounter
Flooding is a confrontational therapy that immerses individuals in their feared stimuli. The therapist exposes the patient to the feared situation or object in a controlled environment, encouraging them to confront their fears head-on. The aim of flooding is to extinguish the fear response through repeated exposure, weakening the connection between the stimulus and the anxiety reaction.
Systematic Desensitization: A Gradual Journey
In contrast, systematic desensitization takes a more gradual approach. The therapist helps the patient create a hierarchy of feared situations, starting with the least anxiety-provoking scenarios and gradually working up to the most intense. Patients learn relaxation techniques, which they use to manage their anxiety during exposure sessions. The therapist provides support and guidance throughout the process, helping the patient develop coping mechanisms and challenge negative thoughts.
Cognitive Involvement: A Key Distinction
A key difference between flooding and systematic desensitization lies in their cognitive involvement. Flooding primarily focuses on extinguishing the fear response through repeated exposure, with minimal emphasis on cognitive processes. Systematic desensitization, on the other hand, integrates cognitive techniques, such as challenging negative thoughts and practicing positive self-talk, to help patients understand and overcome their fears.
Duration and Exposure in Flooding vs. Systematic Desensitization
When it comes to confronting your fears, two effective therapeutic techniques are flooding and systematic desensitization. Each approach takes a distinct approach to extinguishing fear responses, and their durations and exposure methods differ significantly.
Flooding immerses you abruptly and intensely in your feared situation. This rapid and prolonged exposure aims to exhaust your fear response, forcing you to confront its limitations.
Systematic desensitization, on the other hand, takes a more gradual approach. It starts by exposing you to minimal fear-provoking stimuli and gradually increases the intensity over multiple sessions. This 循序渐进 exposure allows you to adjust to the fear gradually, building confidence and reducing your anxiety.
In terms of duration, flooding typically consists of a series of intensive sessions that can last for several hours or even days. Systematic desensitization, however, involves more frequent sessions spread over several weeks or months.
The choice between flooding and systematic desensitization depends on the severity of your fear and your individual needs. If you’re struggling with an intense phobia, flooding may be a more effective option. However, if your anxiety is relatively mild or if you prefer a slower and controlled approach, systematic desensitization might be more suitable.
Cognitive Involvement: Extinguishing Fear and Challenging Negative Thoughts
Flooding
- Limited Cognitive Involvement
- Primarily focused on extinguishing fear through repeated exposure to the dreaded stimulus.
- Minimal emphasis on challenging negative thoughts associated with the fear.
Systematic Desensitization
- High Cognitive Involvement
- Involves a gradual process of exposure accompanied by cognitive restructuring techniques.
- Therapists guide clients to identify and challenge maladaptive thoughts that contribute to their fear.
In systematic desensitization, clients are not only exposed to their fears but also engaged in a collaborative process with their therapist. They delve into the underlying thought patterns that fuel their anxiety and work to develop more rational and adaptive ways of thinking.
Cognitive involvement is crucial in systematic desensitization because it addresses the root cause of fear. By challenging negative thoughts, clients can break the cycle of fear and anxiety. They learn to view their fears with a more balanced perspective, reducing their emotional intensity.
In contrast, flooding does not explicitly target cognitive involvement. While repeated exposure can gradually reduce fear, it may not completely eliminate the underlying negative thoughts. This can increase the likelihood of relapse if clients encounter the feared stimulus again.
Therefore, systematic desensitization’s emphasis on cognitive involvement provides a more comprehensive and durable approach to treating fear and anxiety disorders.
Anxiety During Treatment: The Rollercoaster of Emotions
Flooding vs. Systematic Desensitization: A Tale of Two Exposures
Anxiety disorders often leave sufferers trapped in a cycle of fear and avoidance. Treatment options like flooding and systematic desensitization aim to break this cycle by gradually exposing individuals to their feared stimuli. However, the experience of anxiety during these exposure sessions can differ significantly between the two approaches.
Flooding: A Crash Course in Fear
Flooding is an intense form of exposure therapy that thrusts the individual into the deep end of their fear. Clients are suddenly and fully exposed to the feared object or situation, often without any preparation or coping mechanisms. The goal is to quickly overwhelm the fear response by flooding the person’s system with it. Initially, anxiety can spike to overwhelming levels, but as the exposure continues, the fear gradually diminishes as the threat is repeatedly proven to be non-dangerous.
Systematic Desensitization: A Gentle Ascent
In contrast to flooding, systematic desensitization takes a more gradual approach. Clients are progressively exposed to their fear, starting with the least anxiety-provoking situations and gradually working their way up to the most challenging ones. This allows them to adjust to the anxiety and develop coping strategies along the way. As a result, anxiety tends to be lower during systematic desensitization exposure sessions compared to flooding.
Which Approach Is Right for You?
Ultimately, the choice between flooding and systematic desensitization depends on the individual’s needs and anxiety tolerance.
-
Flooding can be effective for individuals who want to overcome their fear quickly or who have a high tolerance for anxiety.
-
Systematic desensitization is a more gradual option for those who prefer to build coping skills before facing their fears or who have lower anxiety thresholds.
Relapse Prevention: A Comparison Between Flooding and Systematic Desensitization
When treating anxiety disorders, preventing relapse is crucial for lasting recovery. Flooding and systematic desensitization differ in their approaches to relapse prevention.
Flooding: High-Intensity, Limited Cognitive Involvement
Flooding aims to extinguish fear through intense exposure to the feared stimulus. While it doesn’t emphasize cognitive strategies, it may involve homework assignments to practice exposure outside of therapy sessions.
Systematic Desensitization: Gradual Exposure, Cognitive Restructuring
Systematic desensitization involves gradual exposure to the feared stimulus while also challenging negative thoughts and developing coping mechanisms. It places greater emphasis on relapse prevention, including homework assignments, booster sessions, and therapist availability for support.
The Importance of Relapse Prevention Strategies
Both flooding and systematic desensitization recognize the importance of relapse prevention. By implementing strategies that equip individuals with coping mechanisms and ongoing support, these therapies aim to reduce the likelihood of relapse and maintain treatment gains.
Choosing the Right Treatment for Relapse Prevention
The choice between flooding and systematic desensitization for relapse prevention depends on individual needs and preferences.
- Flooding may be suitable for individuals who prefer a faster, more intense approach.
- Systematic desensitization is recommended for those who prefer a gradual, cognitive-based approach with ongoing support.
Consulting with a licensed mental health professional is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for preventing relapse and achieving lasting recovery.
Effectiveness of Flooding and Systematic Desensitization for Specific Anxiety Disorders
Flooding and systematic desensitization are two forms of exposure therapy used to treat phobias and anxiety disorders. Both techniques involve gradually exposing individuals to their feared stimuli, but they differ in their methods and effectiveness for specific disorders.
Flooding is a rapid and intense exposure technique that aims to extinguish fear responses quickly. It involves exposing individuals to their most feared stimuli for prolonged periods without breaks. This can be done in real-life situations or through virtual reality simulations. While flooding can be effective for specific phobias (e.g., fear of spiders, heights), it may be less effective for more complex anxiety disorders.
Systematic desensitization, on the other hand, is a more gradual exposure technique that involves breaking down fears into smaller steps. Individuals are gradually exposed to their feared stimuli, starting with the least anxiety-provoking and working their way up to the most feared. Cognitive techniques are also incorporated to challenge negative thoughts and beliefs associated with the feared stimuli. Systematic desensitization is generally considered more effective for treating complex anxiety disorders (e.g., social anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder).
Research has shown that both flooding and systematic desensitization can be effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety disorders. However, the most effective approach for a particular individual will depend on the type of anxiety disorder, its severity, and the individual’s preferences.
Specific Anxiety Disorders for Which Flooding and Systematic Desensitization Are Most Effective:
- Flooding is most effective for treating specific phobias (e.g., fear of flying, heights, spiders).
- Systematic desensitization is most effective for treating complex anxiety disorders, including:
- Social anxiety disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Safety Considerations in Flooding Therapy
Flooding therapy, an exposure-based treatment for anxiety disorders, involves prolonged exposure to the feared stimuli in a controlled environment. While highly effective, safety considerations must be carefully addressed when implementing flooding therapy.
Individuals with severe anxiety or comorbid conditions are at increased risk during flooding sessions. Panic attacks, breathing difficulties, and fainting can occur in extreme cases. It’s crucial to ensure a safe and supportive environment by:
- Gradually exposing clients to feared stimuli, starting with manageable levels of anxiety.
- Providing constant therapist supervision and monitoring throughout the sessions.
- Establishing clear safety protocols to address any emergencies promptly.
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals (e.g., psychiatrists) to assess and manage comorbid conditions.
Proper screening and assessment before initiating flooding therapy is essential to identify clients who may not be suitable for this approach. It’s important to note that flooding therapy is not recommended for individuals with severe psychotic disorders, active substance abuse, or recent cardiac events.
Therapists must prioritize client safety by carefully evaluating clients’ readiness and monitoring their progress closely. By adhering to these safety measures, flooding therapy can be an effective treatment option for reducing anxiety and improving overall well-being.