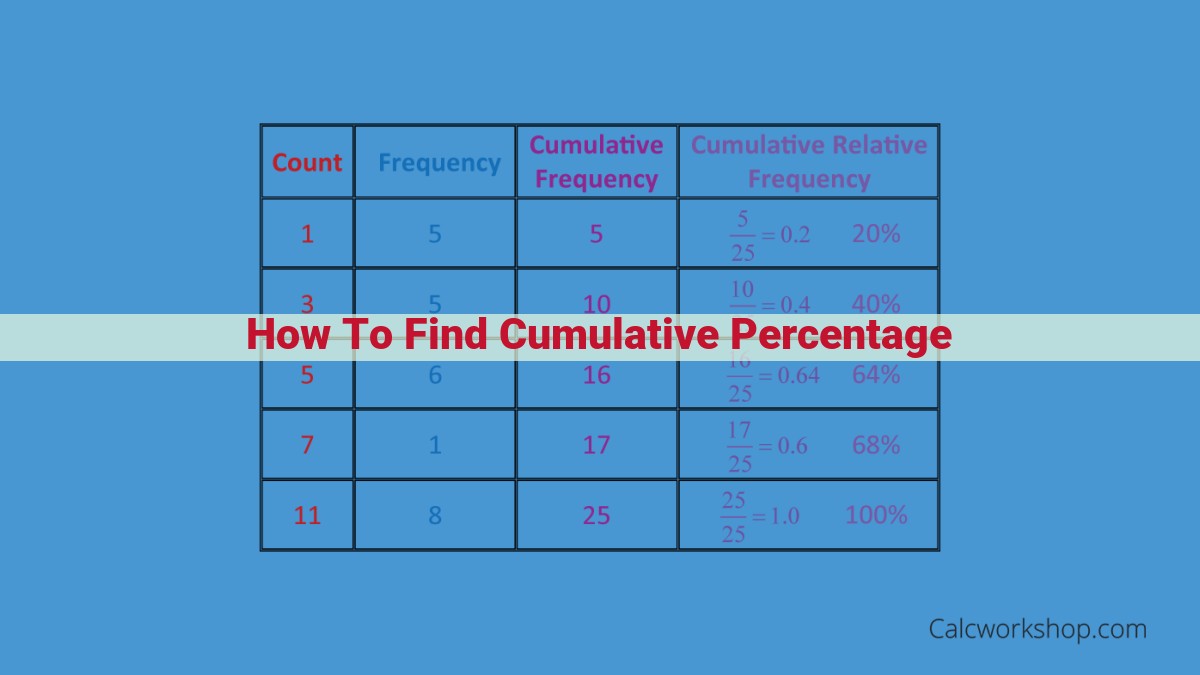
To find cumulative percentage, first determine the target value and its percentage of a base value. Then, add this percentage to any previous percentages to find the cumulative percentage. The formula is (Target Value / Base Value) x 100%. For example, if the base value is 100 and the target value is 25, the percentage is 25%. If a previous percentage was 10%, the cumulative percentage becomes 35%. Cumulative percentage is valuable for tracking progress, calculating averages, and making comparisons. Ensure consistency in calculations and use precise values for accurate results. Consider limitations, such as the potential for misinterpretation and the need for additional context.
Understanding Cumulative Percentage: A Beginner’s Guide
In our data-driven world, understanding how to calculate cumulative percentage is essential for accurate analysis and decision-making. Whether you’re tracking your fitness progress or comparing sales performance, cumulative percentage provides a powerful tool to visualize and interpret data trends.
Key Concepts
Before delving into the calculation process, let’s clarify some key concepts:
- Base Value: The value from which you’re calculating the percentage.
- Target Value: The value you’re comparing to the base value.
- Percentage: The numerical representation of the proportion of the target value to the base value, usually expressed as a value between 0% and 100%.
- Cumulative Percentage: The sum of all percentages calculated up to a particular point in a series of values.
Calculating Cumulative Percentage: A Comprehensive Guide
When analyzing data and tracking progress, cumulative percentage is a valuable metric that provides insights into the accumulation of change over time. This article will guide you through the steps to accurately calculate cumulative percentage, making it easy to understand and apply in real-world scenarios.
Determining Target Value
The first step is to identify the target value, which represents the current or ending point of interest. Target values can range from sales figures to project milestones, depending on the specific context of your analysis. Ensure that the target value is clearly defined and relevant to the data you’re working with.
Finding Percentage of Base Value
Next, you need to determine the percentage of the base value that the target value represents. The base value is typically the starting point or a significant reference point in your data. To calculate the percentage, divide the target value by the base value and multiply by 100. This will give you the percentage of the base value.
Adding Previous Percentages
If you’re calculating cumulative percentage for a series of data points, you need to add the previous percentages to the current percentage. For example, if you’re tracking sales for the past three months, you would add the percentage increase from the first month to the second month to the current percentage for the third month. This cumulative sum represents the total percentage change from the base value.
Calculating Final Cumulative Percentage
Finally, to calculate the final cumulative percentage, simply add the cumulative sum from the previous step to 100%. This will give you the cumulative percentage of the target value compared to the base value. The cumulative percentage provides a clear indication of the total accumulation or change that has occurred over time.
Formula for Calculating Cumulative Percentage
Understanding the concept of cumulative percentage is crucial for various applications in our daily lives. To calculate it accurately, a mathematical formula can be employed. This formula allows us to determine the cumulative percentage by considering the base value, target value, and the previously calculated percentages.
The formula for calculating cumulative percentage is:
Cumulative Percentage = ((Target Value / Base Value) * 100) + Previous Cumulative Percentage
In simpler terms, to calculate the cumulative percentage, we first determine the percentage of the base value represented by the target value. This is achieved by dividing the target value by the base value and multiplying the result by 100. The resulting value is the percentage of the base value.
Next, we add this percentage to the cumulative percentage calculated in the previous step. If this is the first calculation in a series, the previous cumulative percentage will be zero.
For example, let’s say we have a sales target of $10,000 and our current sales are $5,000. To calculate the cumulative percentage, we use the formula:
Cumulative Percentage = ((5000 / 10000) * 100) + 0
Cumulative Percentage = 50%
This means that our current sales represent 50% of our sales target. By using this formula, we can track our progress towards achieving our goal and make informed decisions based on the cumulative percentage calculated.
Example of Calculating Cumulative Percentage
To solidify our understanding of cumulative percentage, let’s dive into a real-life scenario:
Imagine you’re tracking the progress of a marketing campaign. You’ve set a target value of 1,000 conversions. Over the first month, you achieve 250 conversions, which represents 25% of the target value.
Step 1: Determine Target Value
In this example, the target value is 1,000 conversions.
Step 2: Find Percentage of Base Value
The base value is the current progress (250 conversions). The percentage of the base value is 25% (250/1000 * 100).
Step 3: Add Previous Percentages
Since this is the first month, there are no previous percentages to add.
Step 4: Calculate Final Cumulative Percentage
The cumulative percentage up to this point is simply the percentage of the base value, which is 25%.
Therefore, after the first month, the cumulative percentage of conversions achieved is 25%.
Applications of Cumulative Percentage: A Comprehensive Guide
Cumulative percentage is a powerful tool that offers numerous practical applications across various fields. From tracking progress to calculating averages and making comparisons, it plays a vital role in providing insights and informing decision-making.
Tracking Progress
Cumulative percentage can be used to efficiently track progress towards goals. By calculating the cumulative percentage of completed tasks or milestones, individuals and organizations can visualize their advancement and identify areas where additional effort is required. This helps in staying motivated and making timely adjustments to ensure successful outcomes.
Calculating Averages
Cumulative percentage is also useful for calculating averages. By summing the individual percentages and then dividing by the total number of observations, the cumulative average can be obtained. This metric provides a comprehensive measure of performance or achievement, taking into account all the data points in a given set.
Making Comparisons
Cumulative percentage enables comparisons between different sets of data. By calculating the cumulative percentages for each group, it becomes easier to identify trends, patterns, and differences. This is particularly useful when analyzing performance over time, tracking the progress of multiple projects, or evaluating the effectiveness of various strategies.
Tips for Accurate Cumulative Percentage Calculations
Calculating cumulative percentages can be a valuable tool, but it’s important to ensure accuracy in your calculations. Here are some essential tips to help you get it right:
1. Consistency is Key
Maintain consistency when calculating cumulative percentages throughout your data set. Use the same formula and calculation method to avoid any inconsistencies that could skew your results.
2. Precise Values
Accuracy begins with using precise values. Avoid rounding numbers when calculating percentages, as this can accumulate errors. Use the actual, unrounded values for best results.
3. Double-Check Your Work
It’s a good practice to go through your calculations twice. Check each step carefully, ensuring you’ve correctly applied the formula and added the percentages appropriately. This extra effort can prevent common mistakes.
4. Rounding Strategically
If you need to round your final cumulative percentage, do so strategically. Use a consistent rounding method (e.g., rounding to the nearest tenth or hundredth) and always round up when necessary. This ensures you’re not underestimating your percentages.
5. Contextualize Your Results
Remember that cumulative percentages provide a snapshot of a specific data set. To ensure accurate interpretation, consider the context of your results. Determine if the cumulative percentage represents a substantial or insignificant portion of the data to avoid drawing misleading conclusions.
Limitations and Considerations of Cumulative Percentage
While cumulative percentage offers a valuable tool for tracking progress and making comparisons, it’s crucial to be aware of its limitations and considerations.
Potential for Misinterpretation:
Cumulative percentages can sometimes be misinterpreted as absolute percentages. Misinterpreting cumulative percentages can lead to incorrect conclusions or decisions. For instance, if you observe a cumulative growth rate of 50% over three years, it doesn’t imply that the growth rate was constant at 50% each year. The cumulative percentage represents the total growth accumulated over the entire period.
Need for Additional Context:
Cumulative percentages alone may not provide sufficient context to understand the underlying data. Consider the example of tracking sales growth. A cumulative sales growth of 20% over the past five years might seem impressive. However, without additional information, such as overall market conditions or competitor performance, it’s difficult to determine the significance of this growth.
Non-Linearity:
Cumulative percentages assume a linear progression of data. However, in real-world scenarios, data may not always follow a consistent pattern. Fluctuations or sudden changes can impact the accuracy of cumulative percentages. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the non-linearity of data when interpreting cumulative percentages.
Sensitivity to Data Changes:
Cumulative percentages are highly sensitive to changes in the underlying data. Even small adjustments can significantly alter the cumulative percentage. Hence, caution is necessary when making inferences based on cumulative percentages calculated from dynamic or frequently changing data.
Cumulative percentage serves as a useful metric for tracking progress and making comparisons. However, it’s essential to use it with caution and be aware of its limitations and considerations. By understanding the potential for misinterpretation, need for additional context, non-linearity, and sensitivity to data changes, you can ensure that you are using cumulative percentages effectively and drawing accurate conclusions.