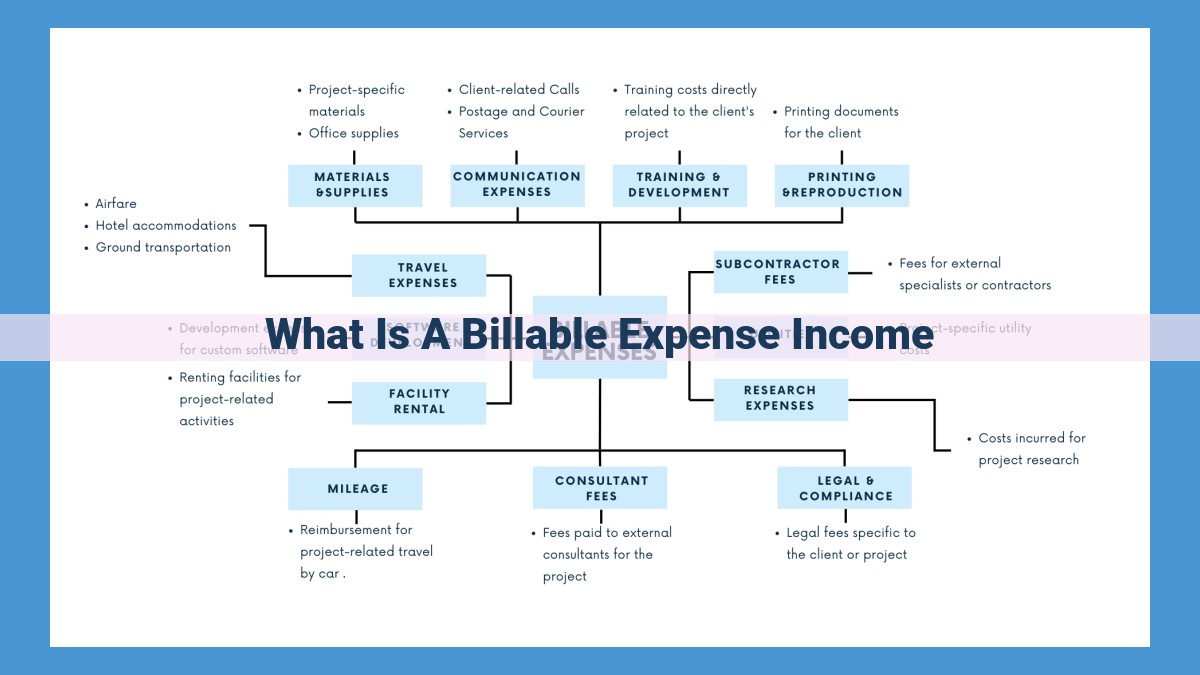
Billable expenses are costs directly related to the provision of goods or services that generate revenue. They are classified as direct, indirect, or overhead expenses. Non-billable expenses, on the other hand, are indirect costs not directly tied to revenue generation. In conjunction with income, billable expenses play a crucial role in calculating gross profit and net income, which is the ultimate bottom line for assessing business profitability.
Billable Expenses: Unveiling Their Impact on Income and Business Success
In the realm of accounting, expenses and income form the bedrock of financial statements, painting a vivid picture of a company’s financial health. Expenses represent the costs incurred by a business to generate revenue, while income symbolizes the inflow of funds from the sale of goods or services. Together, they play a crucial role in determining a company’s profitability and overall financial performance.
Among the myriad of expenses, billable expenses stand out as revenue-generating components, directly tied to the provision of goods or services. These expenses are essential to understand for accurate accounting and effective financial management.
Delving into the Concept of Billable Expenses
Billable expenses are costs that can be directly attributed to the delivery of goods or services. They can be classified into three main categories:
- Direct expenses: These expenses are directly linked to the production of goods or services, such as raw materials, labor costs, and packaging.
- Indirect expenses: These expenses are shared across multiple projects or departments, such as utilities, rent, and insurance.
- Overhead expenses: These expenses are fixed costs that are incurred regardless of production levels, such as administrative salaries and depreciation.
In contrast, non-billable expenses are indirect costs that are not directly related to revenue generation. These include administrative expenses, general expenses, and selling expenses.
The Intricate Relationship between Income and Expenses
Income, the lifeblood of every business, is the inflow of funds from the sale of goods or services. Together, billable expenses and non-billable expenses form the foundation of income calculation.
Gross profit is the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold, which includes direct expenses. Net income is the final bottom line, calculated by deducting all expenses, including both billable and non-billable expenses, from revenue.
The significance of billable expenses lies in their impact on both gross profit and net income. By carefully managing billable expenses, businesses can optimize their revenue and profitability. Conversely, excessive or unnecessary billable expenses can erode profit margins and hinder financial growth.
Understanding the concept of billable expenses is essential for accurate accounting, effective financial management, and ultimately, business success. By tracking and controlling billable expenses, businesses can maximize revenue, improve profit margins, and position themselves for long-term financial health.
Unraveling the Role of Billable Expenses: The Key to Revenue Generation
Understanding income and expenses in accounting is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Billable expenses play a vital role in this financial tapestry, serving as revenue-generating components that directly contribute to a company’s bottom line.
Think of it this way: Imagine a bakery that sells delicious pastries to its loyal customers. The bakery incurs various expenses, such as flour, sugar, and butter, which are essential for creating these delectable treats. These expenses, known as direct billable expenses, are directly tied to the production of the pastries and can be invoiced to customers as part of the final product price. By billing for these expenses, the bakery effectively converts them into revenue.
Just as ingredients are crucial for baking, so too are other expenses that go into running a business. Indirect billable expenses may not be directly incorporated into the final product but are still necessary for providing goods or services. Think of the bakery’s utility bills, rent, and marketing costs. These expenses contribute to the overall operation of the business and can also be billed to customers as separately charged items.
By understanding the concept of billable expenses, businesses can effectively manage their costs and maximize revenue generation. It’s the key to ensuring a healthy financial foundation and achieving long-term profitability.
Billable Expenses: The Key to Understanding Revenue and Profitability
In the realm of accounting, expenses and income play a pivotal role in determining the financial health of a business. Among expenses, billable expenses stand out as revenue-generating components, directly tied to the goods or services provided.
Understanding Billable Expenses
Billable expenses are costs incurred that are directly related to the provision of goods or services. These costs are essential to the operation of a business and are passed on to customers as part of the final price. For instance, if a construction company hires a subcontractor to perform specific tasks on a project, the subcontractor’s fees constitute billable expenses for the construction company.
Classifying Billable Expenses
Billable expenses can be classified into three types:
- Direct expenses: These are costs directly attributable to a specific product or service.
- Indirect expenses: These are costs not directly linked to a specific product or service but necessary for the business’s overall operation.
- Overhead expenses: These are general business expenses, such as rent, utilities, and administrative costs, that cannot be directly attributed to a particular product or service.
Contrasting Non-Billable Expenses
Non-billable expenses, on the other hand, are indirect costs that are not directly related to revenue generation. These expenses include administrative costs, such as salaries of office staff, general expenses such as office supplies, and selling expenses such as marketing and advertising.
The Income-Expense Relationship
Income, or revenue, is the inflow of funds generated from the sale of goods or services. Billable expenses play a crucial role in calculating gross profit and net income. Gross profit is the difference between revenue and the costs directly associated with producing the goods or services (including billable expenses). Net income is the profit left over after deducting all expenses, including both billable and non-billable expenses.
Net Income: The Ultimate Bottom Line
Net income is the ultimate indicator of business profitability. It represents the profit that a business has earned after considering all its costs and expenses. A high net income indicates a profitable business, while a low net income may suggest financial challenges.
Significance of Billable Expenses
Understanding billable expenses is essential for accurate accounting and effective financial management. By carefully tracking and managing billable expenses, businesses can optimize their revenue and profitability. Accurate accounting practices ensure that billable expenses are correctly charged to customers, maximizing revenue. Effective financial management involves controlling expenses, including billable expenses, to minimize their impact on net income.
Classify billable expenses into direct, indirect, and overhead expenses.
The Significance of Billable Expenses in Determining Revenue and Net Income
Unraveling the intricacies of accounting, we often encounter the interplay between expenses and income. Amidst this dynamic, billable expenses emerge as crucial revenue-generating components. Understanding these expenses is paramount for accurate accounting and sound financial management.
Diving into Billable Expenses
Billable expenses encompass costs that are directly tied to the provision of goods or services. They represent the expenditures incurred in the production or delivery of revenue-generating activities. To provide clarity, billable expenses can be categorized into three subcategories:
-
Direct Expenses: Tied directly to the production of each unit sold, such as raw materials or labor costs.
-
Indirect Expenses: Support the overall production process but are not directly attributable to specific units, such as factory rent or utilities.
-
Overhead Expenses: Indirect costs not directly related to production but essential for business operations, such as administrative salaries or marketing expenses.
Non-Billable Expenses: A Distinction
Contrary to billable expenses, non-billable expenses represent indirect costs that are not directly associated with revenue generation. These expenses, often categorized as administrative, general, and selling expenses, are vital for the smooth functioning of a business but do not directly contribute to sales revenue.
The Interplay of Income and Expenses
To fully grasp the significance of billable expenses, we must delve into their role in calculating income. Income refers to the inflow of funds generated from selling goods or services. Billable expenses play a pivotal part in determining gross profit, which is calculated by deducting direct and indirect expenses from revenue. Furthermore, gross profit is used to compute net income, the ultimate measure of business profitability.
Net Income: The Bottom Line
Net income, also known as profit, represents the financial performance of a business after deducting all expenses, including billable and non-billable expenses. It provides a clear indication of the organization’s financial well-being and is a crucial indicator for investors, creditors, and management.
The Impact of Billable Expenses
In conclusion, billable expenses exert a profound impact on both revenue and net income. They represent the costs associated with generating revenue, while non-billable expenses support the overall business operations. Understanding the distinction between these two expense types and their role in calculating profitability is essential for accurate financial reporting and effective business decision-making.
Non-Billable Expenses: The Silent Side of Business
In the world of business, money matters take center stage. Income and expenses are two sides of the same coin, determining a company’s financial health. Often, the spotlight shines brightly on billable expenses, those costs directly tied to revenue generation. However, there’s a lesser-known group that quietly plays a crucial role: non-billable expenses.
Non-billable expenses are like the unsung heroes of the accounting world. They’re costs that aren’t directly associated with generating revenue, but they’re equally important in running a business smoothly. Think of them as the scaffolding that supports the revenue-producing activities.
Administrative expenses are the backbone of everyday operations. They include salaries for office staff, rent, utilities, and office supplies. Without these expenses, the business would grind to a halt. General expenses cover a broader range of overhead costs, such as insurance, legal fees, and accounting services. These expenses keep the business running smoothly and in compliance with regulations. Selling expenses are necessary for marketing and promoting the company’s products or services. They include advertising, sales commissions, and travel expenses. While these expenses don’t directly generate revenue, they’re essential for attracting and retaining customers.
Non-billable expenses may not bring in revenue directly, but they’re crucial for the long-term success of any business. By supporting the revenue-generating activities, they ensure that the company can operate effectively and efficiently. Without these expenses, the business would be like a car without an engine—unable to move forward.
Billable Expenses: A Vital Understanding for Financial Success
In the realm of accounting and finance, expenses and income hold paramount significance. Expenses represent the costs incurred in generating revenue, while income signifies the inflow of funds from sales. Among these expenses, billable expenses stand out as revenue-generating components.
Defining Billable Expenses
Billable expenses are costs directly attributable to providing goods or services. They directly contribute to revenue generation. Examples include raw materials, manufacturing costs, or labor charges for consulting services. These expenses are passed on to the customer as part of the invoice.
Classification of Billable Expenses
Billable expenses can be classified into three categories:
- Direct Expenses: Directly related to the production of goods or services.
- Indirect Expenses: Indirectly related to revenue generation but necessary for business operations.
- Overhead Expenses: General expenses not directly tied to a specific product or service.
Contrast with Non-Billable Expenses
Non-billable expenses, on the other hand, are indirect costs that do not contribute to revenue generation. They include administrative expenses (e.g., salaries of office staff), general expenses (e.g., rent and utilities), and selling expenses (e.g., marketing and sales commissions). These expenses are not passed on to customers and are absorbed by the business as operating costs.
Understanding the Relationship between Income and Expenses
Income, the lifeblood of any business, represents the inflow of funds from sales. Billable expenses are crucial in calculating gross profit and net income. Gross profit is the difference between revenue and billable expenses. Net income, the ultimate bottom line, is the profit remaining after deducting all expenses, including non-billable expenses and other operational costs.
Significance of Billable Expenses
Billable expenses play a pivotal role in determining the profitability of a business. Accurate accounting of these expenses ensures that the business can track revenue and expenses effectively. It provides insights into the financial health of the company and helps decision-makers make informed choices regarding pricing, production, and cost optimization.
Billable expenses are an essential part of financial management. Understanding their significance and proper accounting for them is crucial for accurate financial reporting and business success. By recognizing the difference between billable and non-billable expenses and their relationship to income and net income, individuals and businesses can better manage their finances and maximize profitability.
Billable Expenses: Unraveling Their Significance in Income Generation
In the realm of accounting, expenses and income intertwine like two sides of a coin. Billable expenses stand out as unique revenue-generating components, blurring the lines between costs and income.
The Concept of Billable Expenses
Simply put, billable expenses are costs directly tied to providing goods or services to clients. They represent value added to the products or services you offer. For instance, if you’re a freelance writer, research expenses, software fees, and travel costs for client meetings could qualify as billable expenses.
Non-Billable Expenses: A Contrast
In contrast, non-billable expenses are indirect costs that don’t directly contribute to revenue generation. They include expenses like administrative costs, general expenses, and selling expenses. Think of rent, utilities, and marketing costs that support your business but don’t generate income on their own.
The Relationship between Income and Expenses
Income flows into your business as revenue from selling goods or services. Billable expenses play a crucial role in calculating gross profit and net income. Gross profit is simply sales minus the cost of goods sold (which includes billable expenses). Net income, the ultimate bottom line, is calculated by deducting all expenses (both billable and non-billable) from gross profit.
The Vital Role of Billable Expenses in Unraveling Business Profitability
In the realm of accounting, expenses and income dance a delicate balance, determining the financial health of any organization. Amidst the complex tapestry of costs, billable expenses emerge as revenue-generating components that play a crucial role in the calculation of gross profit and net income.
Billable expenses are costs directly tied to the provision of goods or services. These expenses are charged to clients as part of the invoice, generating revenue for the business. Examples of billable expenses include travel expenses incurred for client meetings, project materials, and subcontractor fees.
In contrast to billable expenses, non-billable expenses are indirect costs that are not directly related to revenue generation. These expenses include administrative costs, such as salaries for accounting staff and office rent, as well as general and selling expenses, such as marketing campaigns and sales commissions. Non-billable expenses are absorbed by the business as part of its overhead costs.
To calculate gross profit, we subtract billable expenses from revenue. Gross profit represents the profit earned before deducting other non-billable expenses and taxes.
Gross Profit = Revenue - Billable Expenses
Net income, the ultimate bottom line of any business, is calculated by deducting all expenses, including both billable and non-billable, from revenue. Net income represents the profit earned after accounting for all costs associated with running the business.
Net Income = Revenue - Billable Expenses - Non-Billable Expenses
Understanding the role of billable expenses is paramount for accurate accounting and financial management. By meticulously tracking and allocating billable expenses, businesses can gain a clear picture of their revenue-generating activities and overall profitability. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, and business expansion.
Billable Expenses and Net Income: Unveiling the Key to Financial Success
In the realm of accounting, understanding the intricacies of billable expenses is crucial for businesses seeking financial prosperity. These expenses, unlike their non-billable counterparts, hold the power to transform costs into revenue-generating engines.
Defining Net Income: The Ultimate Measure of Profitability
At the heart of financial analysis lies net income, a metric that unveils the true measure of a business’s profitability. This figure represents the profit that remains after deducting all expenses, including billable expenses. It serves as the ultimate benchmark for assessing a company’s financial health and success.
In the accounting world, net income is calculated by subtracting the total expenses from the total revenue. By examining this equation, we can clearly see the inverse relationship between expenses and net income: the higher the expenses, the lower the net income.
Billable Expenses: A Catalyst for Net Income Growth
Unlike non-billable expenses that indirectly contribute to business operations, billable expenses directly relate to the provision of goods or services. This vital distinction grants billable expenses the ability to generate revenue.
Imagine a consulting firm that provides marketing services to clients. The costs associated with developing and executing these services, such as staff salaries, travel expenses, and materials, are classified as billable expenses. These expenses are directly tied to the revenue generated from the services provided.
By recognizing the revenue-generating nature of billable expenses, businesses can leverage them to maximize net income. Efficient management of billable expenses, such as optimizing staff utilization and negotiating favorable rates, can significantly boost profitability.
Understanding the role of billable expenses is indispensable for businesses seeking to achieve financial success. These expenses, when meticulously managed, can transform the financial landscape, paving the way for increased revenue, enhanced net income, and ultimately, a thriving enterprise. By embracing the power of billable expenses, businesses can unlock their true earning potential and secure a sustainable future.
The Significance of Billable Expenses: Driving Business Profitability
In the realm of accounting, expenses and income play a crucial role in determining a business’s financial health. Among these expenses, billable expenses stand out as revenue-generating components that directly contribute to the company’s bottom line.
Defining Billable Expenses
Billable expenses are costs incurred in providing goods or services to customers and can be classified into direct, indirect, and overhead expenses. Direct expenses are those directly related to the production of goods or services, such as raw materials and labor. Indirect expenses are those that support the production process but are not directly involved, such as administrative costs and utilities. Overhead expenses are fixed costs that are not directly tied to production, such as rent and insurance.
Contrasting Non-Billable Expenses
Non-billable expenses, on the other hand, are indirect costs that are not directly related to revenue generation. These include administrative expenses, such as salaries and office supplies; general expenses, such as marketing and advertising; and selling expenses, such as commissions and sales support.
The Income-Expense Relationship
Income, the inflow of funds from goods or services sold, plays a key role in determining a business’s profitability. Billable expenses reduce income by deducting their costs from the total amount of revenue generated. This calculation results in gross profit, which represents the profit earned before taking into account other expenses, including non-billable expenses.
After deducting non-billable expenses, the resulting amount is called net income or profit. Net income is the ultimate bottom line and the key indicator of a business’s profitability. It represents the amount of money the business has earned after covering all its expenses, including billable expenses.
Understanding billable expenses is crucial for accurate accounting and financial management. By properly categorizing and tracking these expenses, businesses can gain valuable insights into their costs and revenue streams. This knowledge enables them to optimize their pricing strategies, control expenses, and maximize their profitability. Ultimately, billable expenses play a pivotal role in determining a business’s success and long-term financial health.
Billable Expenses: The Unsung Heroes of Revenue and Net Income
In the intricate dance of accounting, expenses and income are like Yin and Yang, two sides of the same coin. Expenses are the costs incurred during business operations, while income represents the lifeblood that keeps a business afloat. Among the various types of expenses, one often overlooked but critically important category is billable expenses.
Billable Expenses: The Revenue Generators
Unlike non-billable expenses, which are not directly related to revenue generation, billable expenses represent costs that are passed on to customers as part of the price for goods or services rendered. Think of a plumber charging for travel expenses to your home or a lawyer billing for court filing fees. These types of expenses are directly tied to the specific project or service provided.
The Connection between Billable Expenses and Income
The relationship between billable expenses and income is like a two-way street. Billable expenses reduce revenue, as they are deducted from the total amount billed to customers. However, they also contribute to gross profit and net income by increasing the value provided to the client.
Gross profit is calculated by deducting the cost of goods sold from revenue. Billable expenses are included in this calculation, as they are a part of the cost of providing goods or services. The higher the gross profit, the more resources a business has available for other expenses and ultimately, for net income.
Net Income: The Ultimate Measure
Net income, also known as profit, is the holy grail of accounting. It represents the surplus left over after all expenses, including billable expenses, have been paid. A high net income indicates a profitable business, while a low net income can signal financial challenges.
Billable expenses may not be the most glamorous aspect of accounting, but they are pivotal in determining a business’s revenue and profitability. By understanding the direct relationship between billable expenses, income, and net income, business owners can make informed decisions that maximize their financial success. Whether it’s a plumber charging for travel expenses or a lawyer invoicing for research fees, billable expenses are the unsung heroes of every successful business venture.
Billable Expenses: The Key to Accurate Accounting and Financial Management
In the world of accounting, expenses and income are two sides of the same coin. When it comes to revenue generation, billable expenses take center stage. These are costs directly related to providing goods or services, paving the way for additional income and ultimately contributing to the success of any business.
Understanding billable expenses is crucial for accurate accounting and financial management. They play a pivotal role in calculating gross profit and net income, which are key indicators of a business’s financial health. Without a clear grasp of billable expenses, it’s like navigating a stormy sea without a compass – you’re bound to get lost.
For instance, consider a consulting firm that charges clients a fee for its services. The firm’s expenses include travel, lodging, and research. These expenses are directly related to generating revenue for the firm, making them billable expenses. By accurately tracking and allocating billable expenses, the firm can determine the profitability of each client project and make informed decisions about pricing and service offerings.
On the flip side, non-billable expenses are indirect costs that don’t directly contribute to revenue generation. Examples include rent, utilities, and administrative salaries. These expenses are necessary for the overall operation of the business but don’t directly impact income.
By separating billable and non-billable expenses, businesses can gain valuable insights into their financial performance. This allows them to identify areas where costs can be optimized, minimize waste, and maximize profitability. Accurate accounting provides a clear roadmap for financial success, enabling businesses to stay on track and achieve their goals.
In a nutshell, understanding billable expenses is essential for businesses of all sizes. It’s the key to unlocking accurate accounting, ensuring financial stability, and setting the stage for long-term growth and profitability.