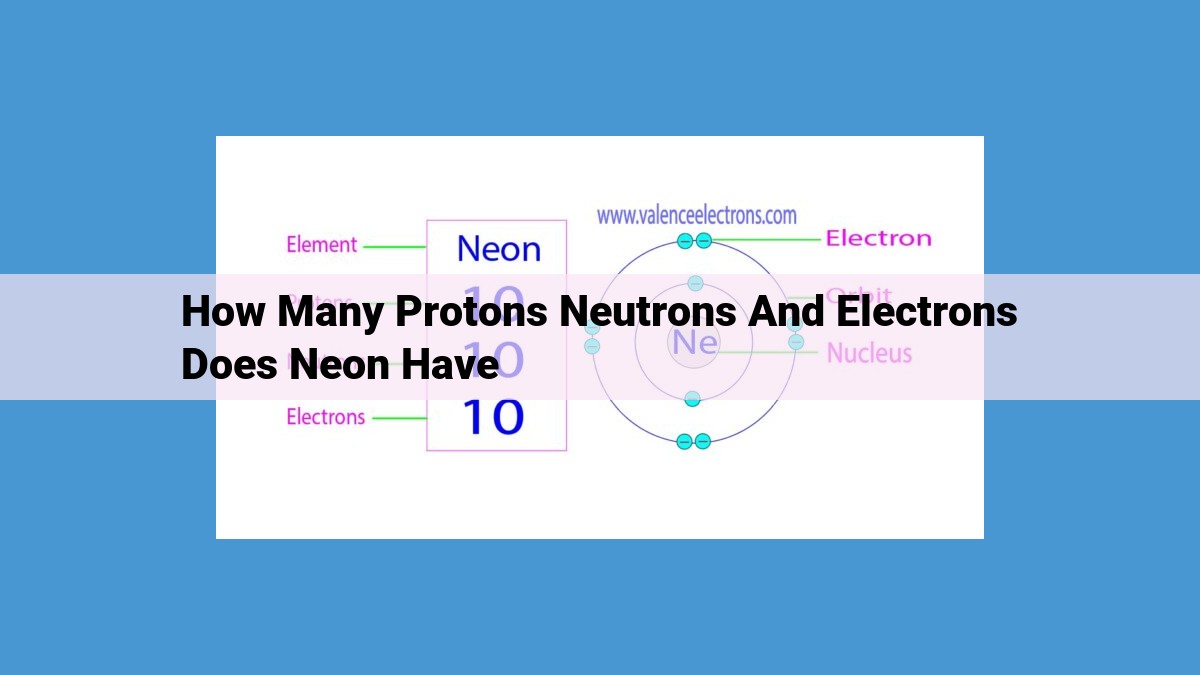
Neon, an element renowned for its unique properties, possesses a distinct number of subatomic particles. Each neon atom comprises 10 positively charged protons, contributing to its mass and defining it as an element. Additionally, 10 uncharged neutrons reside in the nucleus, contributing to its mass variations (isotopes). The outermost regions contain 10 negatively charged electrons, dictating its chemical nature and shaping its interactions with other elements. Understanding these subatomic components is crucial for grasping the behavior and properties of neon, an element employed in diverse applications.
Unveiling the Inner Workings of Neon: A Journey into Subatomic Particles
In the realm of chemistry, understanding the makeup of elements is crucial. At the heart of this understanding lies the knowledge of subatomic particles—protons, neutrons, and electrons. These tiny particles play a fundamental role in defining the properties and behavior of every element, including neon.
Neon, a noble gas known for its vibrant glow, holds a unique arrangement of these subatomic particles that determines its distinctive characteristics. In this blog post, we’ll embark on a storytelling adventure to unravel the secrets of neon’s subatomic composition, exploring the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons it possesses.
Protons in Neon:
- Explain that protons are subatomic particles with a positive charge and mass.
- State that neon has 10 protons.
- Discuss the significance of protons in determining the mass number of an atom and defining the element.
Protons in Neon: The Foundation of an Element
In the realm of chemistry, understanding the subatomic particles that constitute an element is essential. Protons, neutrons, and electrons play a pivotal role in defining the properties and behavior of an element. One such element is neon, a noble gas known for its inertness and distinctive glow.
The Positive Force: Protons in Neon
At the heart of every neon atom lies the positively charged proton. These subatomic particles possess a mass that contributes to the overall mass of the atom. Neon, an element with an atomic number of 10, boasts a total of 10 protons within its nucleus.
The significance of protons extends beyond their mass contribution. They also determine the atomic number of an element. This number, unique to each element, distinguishes one from another. In the case of neon, its 10 protons give it an atomic number of 10, solidifying its identity as an independent element on the periodic table.
Furthermore, protons play a crucial role in defining the mass number of an atom. The mass number represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom and is a distinguishing characteristic for different isotopes of the same element. Isotopes are variations of an element with different mass numbers due to varying neutron counts. In neon, for instance, the most common isotope is neon-20, which has 10 protons and 10 neutrons.
**Neutrons in Neon: The Building Blocks of Isotopes**
In the atomic realm, neutrons play a crucial role in shaping the identity of elements like neon. These subatomic particles, with their neutral charge and a mass comparable to protons, reside within the atom’s nucleus alongside positively charged protons.
Neon harbors 10 neutrons within its nucleus. These neutrons contribute to the atom’s overall mass number, which distinguishes it from other isotopes of the same element. Isotopes are variations of an element with identical atomic numbers (number of protons) but differing mass numbers due to varying neutron counts.
The presence of neutrons is essential for understanding the chemical diversity of elements. While protons determine an element’s atomic number and define its chemical identity, neutrons influence an atom’s mass and affect its stability. Different isotopes of the same element may exhibit varying physical and chemical properties due to their differing neutron counts.
In summary, neutrons are indispensable building blocks that contribute to the mass number and isotopic diversity of elements like neon. Their presence shapes the overall characteristics and behavior of these fundamental building blocks of matter.
**Electrons in Neon: Shaping Chemical Properties**
In the realm of subatomic particles, electrons play a crucial role in defining an element’s identity and behavior. These tiny, negatively charged particles orbit the nucleus of an atom, like celestial bodies around a star. In the case of neon, a noble gas renowned for its distinctive glow, the number and arrangement of electrons hold the key to its unique characteristics.
Neon’s Electronic Structure
Neon possesses 10 electrons, distributed in a specific configuration. These electrons are arranged in two distinct shells, or energy levels. The inner shell holds two electrons, while the outer shell accommodates the remaining eight. This particular electron configuration gives neon a remarkable stability, making it chemically inert and resistant to forming bonds with other elements.
Valency and Reactivity
The number of electrons in an atom’s outer shell determines its valency, which influences its chemical reactivity. Neon’s eight valence electrons signify its reluctance to participate in chemical reactions. This is because the outer shell is completely filled, and the electrons are tightly bound to the atom. As a result, neon exhibits very low reactivity and forms only a handful of compounds under extreme conditions.
Electron Configuration and Behavior
The arrangement of electrons in neon’s shells also affects its physical and chemical properties. The filled outer shell creates a stable electron configuration, which contributes to neon’s inert nature. Additionally, the symmetrical distribution of electrons results in a balanced electrostatic field, making neon a poor conductor of electricity and heat.
Electrons play a pivotal role in shaping neon’s identity and behavior. The presence of 10 electrons, distributed in a specific configuration, defines neon’s chemical inertness, low reactivity, and distinctive glow. Understanding the subatomic composition of neon provides valuable insights into its unique properties and its applications in various fields, ranging from lighting to plasma technology.