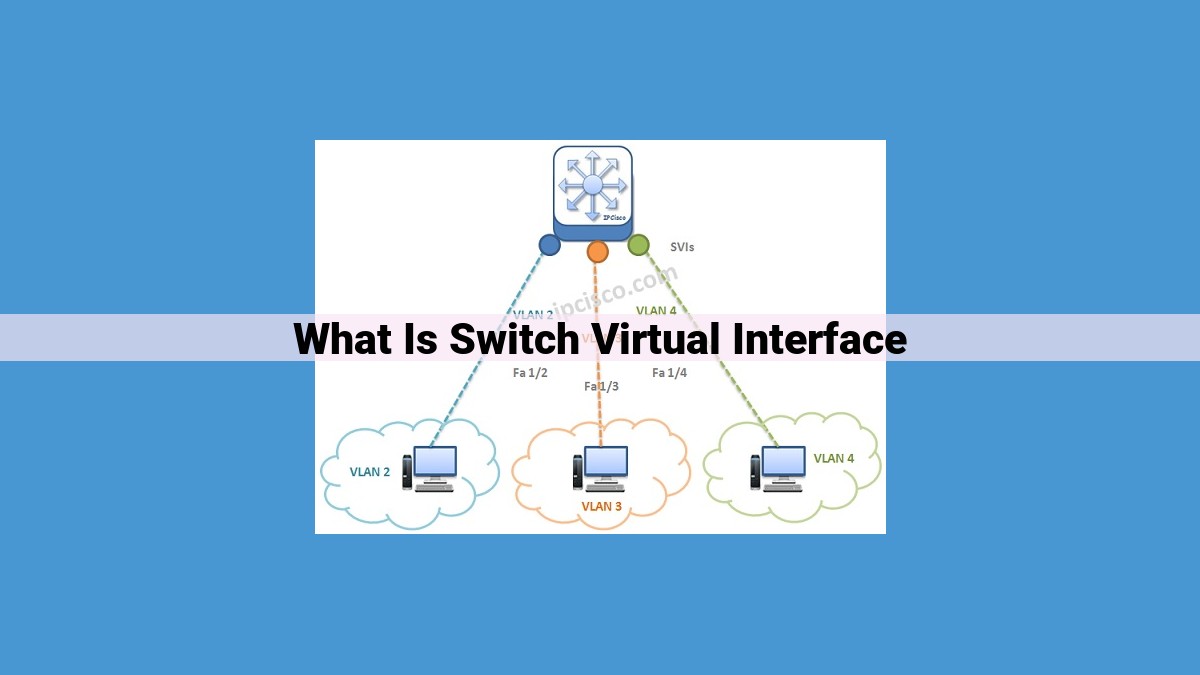
Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs) are virtual interfaces configured on switches to connect VLANs to a shared physical port. SVIs provide IP addressing, routing, and management access to specific VLANs, simplifying network management, enhancing security through VLAN isolation, and improving scalability. They act as a bridge between VLANs and the external network, allowing communication and routing between different VLANs while keeping them isolated.
Defining Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs)
- Explanation of what SVIs are and their purpose in networking.
Defining Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs)
In the captivating tapestry of computer networking, the concept of Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs) emerges as a pivotal thread. These visionary interfaces play a transformative role by weaving the very fabric of VLANs and enabling seamless communication across diverse virtual networks.
SVIs, akin to magical gateways, bridge the gap between physical switches and virtual LANs (VLANs), establishing a harmonious coexistence within the digital realm. They serve as virtual conduits, assigning IP addresses to VLANs and orchestrating the intricate dance of data packets between these virtual domains.
The genesis of SVIs lies in the need for efficient and secure network segmentation. By isolating VLANs, SVIs provide a protective shield against broadcast storms and enhance the overall resilience of the network. Their presence empowers administrators with unprecedented control and flexibility in managing and shaping their network landscapes.
Understanding Related Concepts: VIs, VLANs, and VRFs
To unravel the intrigue of Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs), it’s essential to unveil their close companions: Virtual Interfaces (VIs), Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), and Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRFs). These concepts weave a rich tapestry that enhances SVIs’ functionality and versatility.
VIs are virtual interfaces that reside within a switch, providing a pathway for data to flow between different network segments. They act as software-defined interfaces, enabling a single physical switch port to support multiple logical interfaces. This flexibility allows administrators to create and manage network segments without the need for additional hardware.
VLANs, on the other hand, are logical networks that segment a physical switch into multiple isolated broadcast domains. They partition a switch’s traffic into distinct groups, preventing communication between devices in different VLANs. By assigning SVIs to VLANs, administrators can extend the reach of IP connectivity to these isolated networks, enabling inter-VLAN routing.
VRFs, short for Virtual Routing and Forwarding, provide an additional layer of isolation and segmentation within a network. They create isolated routing tables within a single router, allowing multiple virtual networks to coexist and communicate independently. SVIs can be assigned to VRFs, further enhancing traffic isolation and security. By understanding these related concepts, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the crucial role SVIs play in modern networking environments.
The Mighty Role of SVIs in Network Mastery
In the realm of networking, Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs) emerge as unsung heroes, playing a pivotal role in managing and connecting Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs). These interfaces, when configured, transform switches into powerful routers, bridging the gaps between VLANs, and providing access to the outside world.
Assigning IP Addresses to VLANs: The Foundation of Connectivity
One of the key functions of SVIs is to bestow IP addresses upon VLANs. Without an IP address, devices cannot communicate, and VLANs would remain isolated islands, unable to connect to the broader network. By assigning unique IP addresses to each VLAN, SVIs enable seamless communication between VLANs and the outside world.
Routing Traffic Between VLANs: Unifying the Network’s Fabric
SVIs don’t stop at assigning IP addresses; they go a step further by routing traffic between VLANs. A switch, equipped with SVIs, can swiftly forward packets between different VLANs, allowing devices to communicate across network boundaries. This inter-VLAN routing capability is crucial for creating a cohesive network fabric where devices can collaborate and share resources.
Enabling Management Access: The Gateway to Control
SVIs also serve as gateways for management access to the switch. By configuring an SVI with an IP address, network administrators can remotely connect to the switch and perform essential management tasks, such as monitoring, configuration changes, and troubleshooting. This remote access capability simplifies network management and ensures optimal performance.
SVIs are the keystone of network architecture, empowering switches with the capabilities of routers. They assign IP addresses, facilitate inter-VLAN routing, and provide management access. By harnessing the power of SVIs, network administrators can create flexible, scalable, and secure networks that meet the demands of modern IT environments.
Unlocking the Power of Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs): Benefits for Your Network’s Performance
In the realm of networking, achieving efficiency and security is crucial. Among the key elements that empower these goals are Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs). Let’s delve into the myriad benefits SVIs bring to the table, making them indispensable tools for any network administrator.
Simplified Network Management: A Breeze for Administrators
SVIs simplify network management by offering a centralized point of control for multiple VLANs. Rather than managing individual VLANs separately, you can assign IP addresses to entire VLANs through SVIs. This not only streamlines the configuration process but also reduces the risk of errors, enhancing overall network efficiency.
Enhanced Security: Isolating VLANs for Peace of Mind
Security is paramount in today’s connected world. SVIs bolster network security by enabling VLAN isolation. Each SVI serves as a gateway for a specific VLAN, isolating traffic between VLANs. This prevents unauthorized access and ensures the confidentiality of sensitive data, providing peace of mind for network administrators.
Improved Scalability: Accommodating Network Growth Seamlessly
As networks grow in size and complexity, scalability becomes imperative. SVIs facilitate network scalability by allowing the addition of new VLANs without the need for physical interfaces. This flexibility enables network administrators to adapt to changing requirements, accommodate new devices, and expand the network seamlessly.
Configuring Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs)
Creating an SVI
SVIs are created on the switch using the interface vlan command. The VLAN ID is specified as the argument to the command. For example, to create an SVI for VLAN 10:
interface vlan 10
Configuring an SVI
Once the SVI is created, it can be configured with an IP address and subnet mask using the ip address command. The IP address should be in the same subnet as the devices that will be connected to the VLAN. For example, to configure the SVI for VLAN 10 with the IP address 192.168.10.1 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0:
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Verifying the SVI Configuration
The SVI configuration can be verified using the show ip interface brief command. This command will display a list of all the SVIs on the switch, along with their IP addresses, subnet masks, and operational status. For example:
show ip interface brief
...
VLAN10 up up 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
...
Sample Configuration Commands
The following are sample configuration commands for creating, configuring, and verifying an SVI:
interface vlan 10
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
show ip interface brief