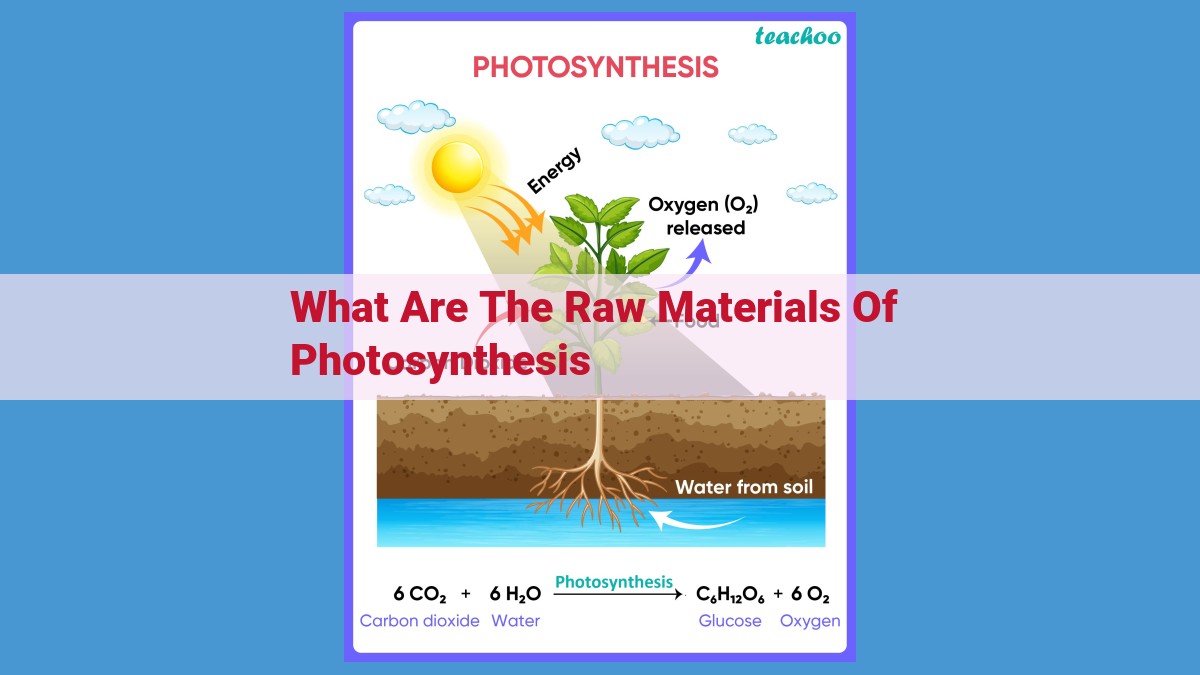
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, relies on three essential raw materials: water, carbon dioxide, and light energy. Water provides hydrogen and oxygen atoms for glucose production, while carbon dioxide serves as the primary carbon source. Light energy drives the process, providing the activation energy needed to transform these raw materials into glucose. Photosynthesis is crucial for producing food for all living organisms on Earth and plays a vital role in maintaining the planet’s oxygen balance.
Water: The Life-Giving Source for Photosynthesis
In the realm of life’s intricate tapestry, where the dance of nature unfolds, a remarkable process called photosynthesis takes center stage. It is here, in the verdant embrace of plants, that life’s sustenance is forged from the raw elements of the Earth.
At the heart of this wondrous transformation lies water, the life-giving elixir that bestows its vital essence upon the photosynthetic dance. Within the depths of its molecular structure reside the building blocks that give rise to glucose, the primary fuel for life on our planet.
Water molecules, composed of two hydrogen atoms bound to an oxygen atom, serve as the primary source of both hydrogen and oxygen in the photosynthetic equation.
- Hydrogen atoms, with their single electron, eagerly join forces with carbon atoms, the backbone of glucose, forming the essential scaffolding for this vital molecule.
- Oxygen atoms, on the other hand, play a dual role: not only do they contribute to the formation of glucose, but they also serve as the byproduct of photosynthesis, released into the atmosphere to sustain the breath of life.
Thus, without the presence of water, the photosynthetic symphony would falter, and the very foundation of life would crumble.
Water, the humble and unassuming molecule, stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of all living things, a vital cog in the چرخه بیوشیمیایی that sustains our planet’s intricate web of life.
Carbon Dioxide: The Source of Carbon for Glucose Synthesis
Photosynthesis, the remarkable process that fuels life on Earth, requires three essential elements: water, carbon dioxide, and light energy. Carbon dioxide plays a pivotal role as the main source of carbon for the synthesis of glucose, the primary energy source for plants, animals, and humans.
Imagine carbon dioxide as the building blocks of glucose. Each molecule of glucose contains six carbon atoms, and these atoms are derived from carbon dioxide. During photosynthesis, this gas is absorbed from the atmosphere through tiny pores on plant leaves. Inside these leaves, carbon dioxide encounters other reactants in specialized organelles called chloroplasts.
Enzymes within the chloroplasts facilitate a series of complex chemical reactions that transform carbon dioxide into glucose. This process is known as the Calvin cycle. It begins with the enzyme RuBisCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) binding carbon dioxide to a five-carbon sugar called ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). This reaction forms two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
The 3-PGA molecules undergo a series of enzymatic transformations, including phosphorylation, reduction, and isomerization, to ultimately produce glucose. This precious sugar serves as the foundation for plant growth and development. It provides energy for cellular processes and is also converted into other essential molecules, such as starch, cellulose, and proteins.
Without carbon dioxide, the synthesis of glucose would not be possible. Plants would be unable to capture the sun’s energy and convert it into food, leading to a catastrophic collapse of the Earth’s ecosystems.
Light Energy: The Vital Spark in Photosynthesis
In the photosynthetic dance of life, water, carbon dioxide, and chlorophyll are central characters. But there’s another critical element that serves as the driving force of this verdant symphony: light energy. This radiant power fuels the intricate chemical transformations that create glucose, the foundation of nourishment for all living beings.
Light energy comes in a kaleidoscope of colors and wavelengths, but for photosynthesis, it’s primarily the blue and red wavelengths that hold the key. These photons, once absorbed by chlorophyll molecules within plant cells, energize electrons. Like miniature sparks, these charged particles embark on an extraordinary journey, carrying the energy needed to separate hydrogen atoms from water molecules and carbon atoms from carbon dioxide molecules.
This energy-rich separation sets the stage for the construction of glucose molecules. Hydrogen atoms combine with carbon dioxide to form complex carbohydrate chains, while the liberated oxygen atoms are released into the atmosphere, providing the vital breath of life for us and countless other organisms.
The different wavelengths of light energy play specific roles in the photosynthetic process. Blue light primarily drives the splitting of water molecules, releasing oxygen and hydrogen. Red light, on the other hand, is crucial for the conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose.
In essence, light energy is the conductor that orchestrates the photosynthetic symphony, transforming dull water and carbon dioxide into the life-sustaining glucose that nourishes the planet. Without this radiant power, the tapestry of life would unravel, leaving behind a barren and desolate world.
**Photosynthesis: The Lifeline of Life on Earth**
In the intricate tapestry of life, photosynthesis stands as a cornerstone process essential for the very existence of our planet’s ecosystems. This remarkable process, performed primarily by plants, algae, and certain bacteria, underpins the production of food for not only plants themselves but also for the majority of animals and humans.
Imagine our world without photosynthesis. The verdant landscapes we cherish, the nourishing fruits and vegetables that sustain us, and the very air we breathe would simply cease to be. Without this life-giving process, the delicate balance of our planet would crumble, leaving an uninhabitable wasteland in its wake.
Photosynthesis, in its essence, is a complex chemical reaction that harnesses the energy of sunlight to transform water and carbon dioxide into glucose, the primary energy source for all living organisms. Through this process, plants produce oxygen as a byproduct, which is vital for the respiration of all aerobic organisms, including ourselves.
The role of photosynthesis in food production cannot be overstated. As the primary producers in the food chain, plants utilize photosynthesis to synthesize the carbohydrates that sustain them. These carbohydrates, in turn, become the food source for herbivorous animals, who then serve as sustenance for carnivores and omnivores. Ultimately, all life on Earth is inextricably linked to the photosynthetic process.
Moreover, photosynthesis plays a pivotal role in regulating Earth’s atmosphere. By absorbing carbon dioxide during the process, plants help to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas levels. Additionally, the oxygen produced by photosynthesis replenishes the atmosphere, ensuring its purity and supporting the respiratory needs of all living creatures.
The importance of photosynthesis extends beyond its ecological significance. It is also a fundamental process in the biogeochemical cycles that govern our planet’s life-support systems. By incorporating carbon into organic molecules, photosynthesis contributes to the cycling of carbon through the atmosphere, oceans, and terrestrial ecosystems. This process helps to maintain a stable global carbon balance and prevents atmospheric CO2 levels from reaching harmful levels.
In conclusion, photosynthesis is an indispensable process that underpins the very fabric of life on Earth. It is the cornerstone of food production, sustains the oxygen cycle, and plays a crucial role in regulating our planet’s atmosphere. Preserving and promoting photosynthesis is paramount to ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of our planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants.
Threats to Photosynthesis
- Discuss potential threats to photosynthesis, such as pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction.
Threats to the Vital Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, the cornerstone of life on Earth, faces numerous threats that jeopardize its critical role in sustaining our planet. From the insidious effects of pollution to the devastating impacts of climate change, the very foundation of our ecosystem is at risk.
Pollution: A Toxic Assault on Photosynthesis
Air and water pollution pose significant threats to photosynthesis. Industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural practices release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere and water bodies, damaging plant tissues and hindering their ability to absorb sunlight. These pollutants can accumulate in plant leaves, impairing their energy conversion efficiency and ultimately reducing glucose production.
Climate Change: A Threatening Alteration of Conditions
Rising global temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns associated with climate change have profound implications for photosynthesis. Extreme temperatures can stress plants, making them more susceptible to disease and reducing their photosynthetic activity. Prolonged droughts can deprive plants of the water they need for photosynthesis, leading to wilting, stunted growth, and ultimately reduced food production.
Habitat Destruction: A Loss of Green Infrastructure
The relentless expansion of human activities, such as urbanization and deforestation, contributes to habitat destruction, eliminating vast areas of vegetation that serve as vital centers for photosynthesis. The loss of these green spaces reduces the Earth’s capacity to produce oxygen and store carbon, further exacerbating the threats to photosynthesis.
Protecting Photosynthesis for a Sustainable Future
The preservation of photosynthesis is imperative for the well-being of our planet and its inhabitants. By mitigating pollution, addressing climate change, and protecting natural habitats, we can safeguard this vital process and ensure the continued provision of oxygen, food, and a stable environment for generations to come.
Call to Action: Promoting Photosynthesis in Our Own Spaces
While global efforts are crucial, we can also contribute to the preservation of photosynthesis in our immediate surroundings. By planting trees and supporting green initiatives, we create pockets of photosynthetic activity that mitigate pollution, sequester carbon, and provide valuable habitats. Embracing sustainable practices in our homes and gardens, such as using organic fertilizers and reducing water consumption, can also foster healthy plant growth and promote efficient photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis, the life-sustaining process that provides the foundation for our ecosystem, faces a plethora of threats. Pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction are formidable challenges that must be addressed to ensure its preservation. By understanding these threats and taking proactive measures, we can protect photosynthesis and safeguard the vitality and sustainability of our planet for generations to come.
Promoting Photosynthesis: A Vital Step Towards Sustainable Living
Photosynthesis, the fundamental process by which plants convert sunlight into energy-rich nutrients, is the cornerstone of life on Earth. It generates the oxygen we breathe and nourishes every living creature in its path. However, human activities, such as pollution and deforestation, pose significant threats to this crucial process. The well-being of our planet depends on our collective efforts to protect and promote photosynthesis.
In our own homes and gardens, we can play a vital role in fostering this life-giving process. Here are some practical tips:
1. Plant Trees and Greenery: Trees and other plants are the primary agents of photosynthesis. By planting trees in our yards and communities, we increase the amount of available chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for absorbing sunlight.
2. Create a Wildlife-Friendly Environment: Insects and birds are essential pollinators, aiding in the transfer of pollen between plants. Provide nesting boxes and bird feeders to attract these beneficial creatures and support their role in plant reproduction.
3. Use Organic Fertilizer: Inorganic fertilizers can lead to soil acidification, which inhibits plant growth and reduces photosynthesis. Opt for organic fertilizers that release nutrients slowly and promote soil health.
4. Conserve Water: Water is a vital reactant in photosynthesis. Implement water-saving techniques such as mulching, drip irrigation, and rainwater harvesting to ensure plants have adequate moisture.
5. Reduce Pollution: Air pollution, particularly from vehicles and industrial emissions, can damage plant leaves and impair photosynthesis. To mitigate this impact, promote public transportation, cycling, and other eco-friendly alternatives.
6. Support Sustainable Agriculture: Choose to purchase produce from farmers who employ sustainable farming practices that prioritize soil health and minimize chemical inputs. This supports both photosynthesis and the livelihoods of local farmers.
7. Educate and Inspire: Share the importance of photosynthesis with friends, family, and neighbors. Encourage others to engage in gardening and make informed choices that protect our planet’s life-giving processes.
By integrating these tips into our daily lives, we can create a more conducive environment for photosynthesis, ensuring the well-being of our planet and future generations. Let us all be ambassadors for this vital process, safeguarding the source of life for all living creatures.