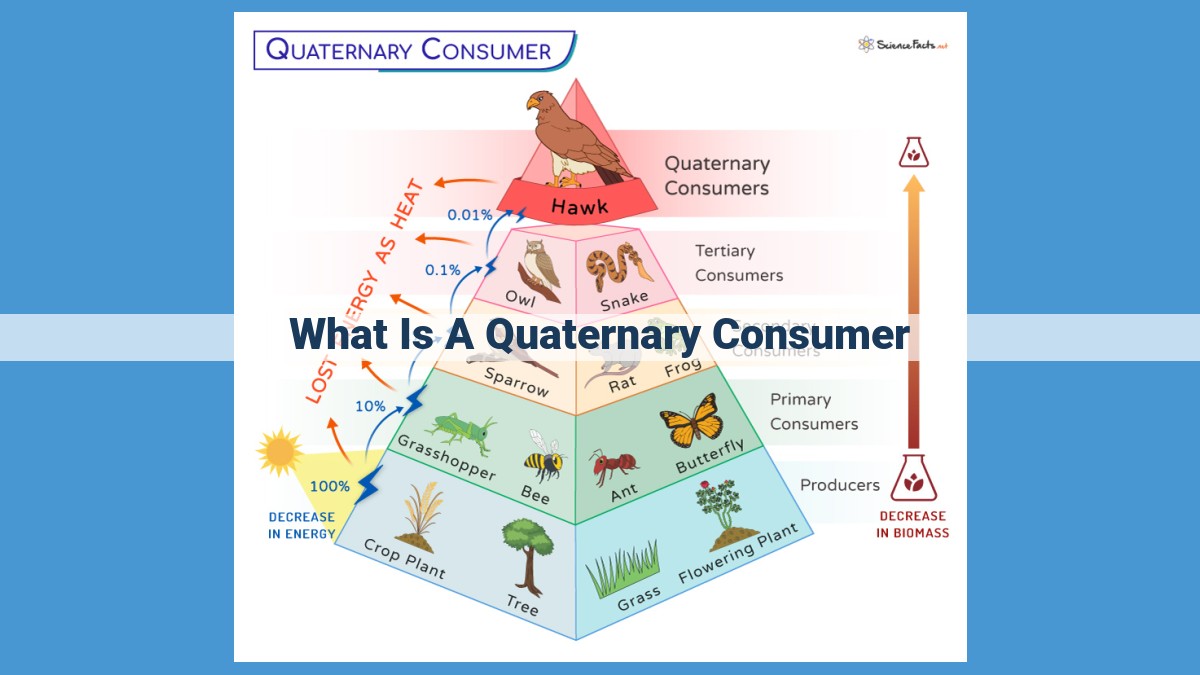
Quaternary consumers are apex predators that occupy the fourth trophic level in food chains, preying on tertiary consumers. They play a crucial role in ecosystem balance by controlling secondary consumer populations and facilitating nutrient cycling. Their specialized ecological niches and examples include large predators like wolves, lions, and killer whales. As key regulators of food webs, their removal or decline can disrupt ecosystem stability and functioning. Conservation efforts are essential to protect these apex predators from threats such as habitat loss and hunting, ensuring the health and balance of ecosystems.
Quaternary Consumers: Apex Predators in the Ecosystem
In the intricate tapestry of life, each species occupies a unique niche, playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Quaternary consumers stand at the pinnacle of food chains, their formidable presence shaping the very fabric of the environments they inhabit. Let us delve into their fascinating world and unravel their importance.
Trophic Levels and Quaternary Consumers
Food chains are linear representations of the flow of nutrients and energy through an ecosystem. Each level in this chain is known as a trophic level. Quaternary consumers occupy the fourth trophic level, feeding primarily on tertiary consumers. These apex predators are the ultimate consumers, with no natural predators of their own.
Ecological Importance of Quaternary Consumers
Quaternary consumers are essential for ecosystem stability. They play a critical role in controlling secondary consumer populations, thereby preventing overpopulation and maintaining a healthy balance within the food web. Their presence also facilitates nutrient cycling, as they consume prey species that have accumulated nutrients from lower trophic levels. By doing so, they help distribute these nutrients throughout the ecosystem.
Role of Quaternary Consumers in Maintaining Ecosystem Balance
Quaternary consumers, the apex predators in an ecosystem, play a vital role in maintaining its delicate equilibrium. Their presence at the top of the food chain exerts a profound influence on the entire ecosystem, ensuring its stability and functionality. Here’s how these formidable hunters contribute to the health of our planet:
Controlling Secondary Consumer Populations
Quaternary consumers prey upon secondary consumers, such as carnivores and omnivores. This predation helps regulate their populations, preventing them from overexploiting primary consumers, such as herbivores. In the absence of quaternary consumers, secondary consumers could multiply unchecked, devastating plant populations and disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
Facilitating Nutrient Cycling
The predation by quaternary consumers also plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling. When they consume prey, they break down organic matter and release nutrients back into the environment. These nutrients can then be utilized by plants, fueling their growth and supporting the entire food chain. Without quaternary consumers, nutrient cycling would be disrupted, leading to a decline in plant productivity and overall ecosystem health.
In conclusion, quaternary consumers are indispensable components of ecosystems. Their role in controlling secondary consumer populations and facilitating nutrient cycling ensures the balance and stability of these complex natural systems. Their presence is essential for maintaining healthy and resilient ecosystems that support a diverse array of life forms.
Ecological Niche and Examples: Quaternary Consumers in the Food Web
Quaternary consumers, residing at the pinnacle of the food chain, occupy specialized ecological niches that drive the balance and functioning of ecosystems. These apex predators, the ultimate hunters, exhibit remarkable adaptations and behaviors that enable them to thrive in their respective environments.
Lions:
In the vast grasslands of Africa, lions rule as the ultimate quaternary consumers. These majestic predators possess exceptional hunting skills and social structures. They coordinate strategic attacks, working together to bring down large prey such as wildebeest and zebras. By controlling these populations, lions prevent overgrazing and maintain the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Orcas:
The frigid waters of the ocean are home to another apex predator, the orca. These highly intelligent marine mammals possess a diverse diet that includes seals, fish, and even other whales. Orcas are known for their advanced hunting techniques, such as breaching to stun prey and using their powerful tails to create powerful waves that wash their victims ashore. Their presence ensures the health and balance of marine ecosystems.
Golden Eagles:
Soaring high above rugged mountains, golden eagles are the masters of the sky. These birds of prey have exceptional eyesight and aerodynamic abilities, allowing them to spot prey from great distances. Their diet consists primarily of small mammals, which they snatch with their powerful talons. Golden eagles play a vital role in controlling rodent populations and maintaining the health of mountain ecosystems.
Quaternary consumers are the cornerstones of ecosystems, shaping the composition and balance of food webs. Their specialized ecological niches, honed over millions of years of evolution, contribute to the stability and resilience of our natural world. However, these apex predators face threats such as habitat loss and hunting, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts to safeguard their presence and ensure the continued health of our planet.
Significance of Quaternary Consumers in Food Webs
In the intricate tapestry of ecosystems, quaternary consumers play a pivotal role as the apex predators, occupying the highest trophic level. Their presence exerts a profound influence on the stability and functioning of food webs.
Quaternary consumers keep secondary consumer populations in check. Without these formidable predators, secondary consumers would overpopulate and deplete the resources of primary consumers, leading to a cascade of imbalances throughout the ecosystem. They act as a buffer, preventing unchecked growth that could disrupt the delicate equilibrium of the food web.
Moreover, the predation of quaternary consumers on secondary consumers facilitates nutrient cycling. When they consume their prey, they extract vital nutrients that are eventually returned to the ecosystem through their waste products. This process enriches the soil and supports plant growth, creating a nutrient cascade that benefits the entire web of life.
The role of quaternary consumers as regulators of food webs is indispensable. Their removal or decline can have devastating consequences, disrupting the balance of the ecosystem and potentially leading to population explosions of secondary consumers. This can result in overgrazing, habitat degradation, and a loss of biodiversity. Therefore, it is crucial to protect and conserve these apex predators to ensure the stability and resilience of our ecosystems.
Threats to Quaternary Consumers
Quaternary consumers, as apex predators, face a unique set of challenges that threaten their survival. Habitat loss poses a major threat to these species, as their specialized ecological niches often require vast territories for hunting and breeding. Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and habitat fragmentation, significantly reduce the availability of suitable habitats for quaternary consumers.
Hunting is another major threat, especially for large, charismatic species that are often targeted by trophy hunters. These predators are often slow-reproducing and have low population densities, making them vulnerable to overhunting. Poaching for their pelts, claws, or other body parts can also deplete populations of quaternary consumers.
Conservation of Quaternary Consumers
Conserving quaternary consumers is crucial for the health and stability of ecosystems. Their presence helps to regulate lower trophic levels and maintain biodiversity. Protecting their habitats, reducing hunting pressure, and combating poaching are essential conservation measures. Establishing protected areas and implementing sustainable land use practices can help secure the survival of these apex predators.
Education and awareness are also vital for conservation efforts. By fostering an understanding of their ecological importance and the threats they face, we can mobilize public support for their protection. Collaborations between conservation organizations, governments, and local communities are crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and ensuring the long-term survival of quaternary consumers.
In addition to direct threats, climate change is also emerging as a significant threat to quaternary consumers. Shifting weather patterns, rising temperatures, and altered prey distributions can disrupt their ecological balance and lead to population decline. Adaptive conservation measures, such as protected areas that encompass predicted species ranges under future climate scenarios, are essential for mitigating the impacts of climate change on these apex predators.