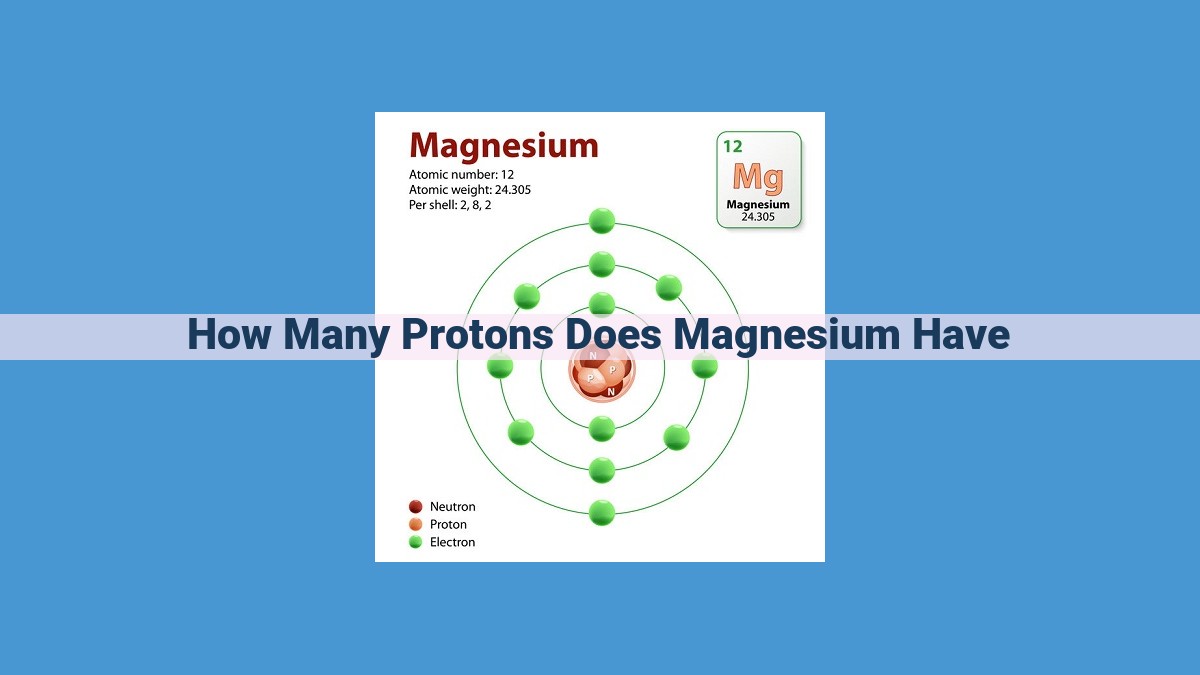
Magnesium’s proton count is determined by its atomic number, which is 12. Protons are subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom and define its identity. Magnesium’s 12 protons distinguish it as a unique element with specific chemical properties and behavior.
Understanding Protons
Protons, the cornerstones of atomic structure, are positively charged subatomic particles nestled within an atom’s nucleus alongside their neutron counterparts. Protons play a pivotal role in shaping the identity and behavior of an element.
The heart of this article lies in the exploration of protons, with particular focus on determining the proton count in magnesium, a versatile and abundant element found in countless applications around us.
Atomic Number: The Key to Proton Count
In the realm of chemistry, determining the number of protons in an atom is crucial for understanding its elemental identity and behavior. The atomic number plays a pivotal role in this endeavor, serving as the cornerstone for unraveling the proton count.
Defining Atomic Number
The atomic number, denoted by the symbol Z, is an integer assigned to each element in the periodic table. It represents the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. The nucleus, located at the heart of the atom, houses protons and neutrons, which are collectively known as nucleons.
Significance of Atomic Number
The atomic number is not merely a numerical label; it holds profound significance in the world of chemistry. It has been recognized as a fundamental characteristic of elements, as it:
- Identifies elements: Each element has a unique atomic number, distinguishing it from all other elements. For instance, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, while helium has an atomic number of 2.
- Classifies elements: The atomic number serves as the basis for organizing elements into the periodic table. Elements with similar atomic numbers share similar chemical properties and are grouped together.
- Predicts chemical behavior: The atomic number influences the chemical behavior of an element. It determines the number of electrons in the atom’s electron cloud, which in turn affects its reactivity and bonding capabilities.
Related Concepts: Proton Number and Nuclear Charge
The atomic number is closely intertwined with two related concepts:
- Proton number: The proton number is synonymous with the atomic number. It refers to the total number of protons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Nuclear charge: The nuclear charge is the net positive charge of an atom’s nucleus. It arises from the presence of protons, as protons carry a positive charge.
In essence, the atomic number serves as a roadmap to understanding the proton count in an atom. It provides a numerical representation of the number of protons, which in turn reveals the element’s identity, classifies it within the periodic table, and influences its chemical behavior.
Determining the Proton Count in Magnesium: Unraveling the Atomic Puzzle
In the realm of atoms, protons play a crucial role. They reside in the atomic nucleus, the heart of an atom, and hold a positive electric charge. Understanding protons is essential for comprehending the fundamental structure and behavior of matter.
Atomic Number: The Gateway to Proton Count
The atomic number of an element is a unique identifier that reveals the number of protons in its nucleus. This number also represents the number of nuclear charge, which is the sum of the positive charges carried by the protons. For any given element, the atomic number remains constant, providing a distinctive fingerprint that differentiates it from all other elements.
Magnesium’s Atomic Number: A Tale of Twelve
Magnesium is a silvery-white metal with a wide range of applications, from lightweight alloys to essential biological functions. The atomic number of magnesium is 12. This means that every magnesium atom in existence possesses 12 protons in its nucleus.
The Significance of Proton Count: The Essence of Identity
The number of protons in an atom profoundly influences its chemical properties and behavior. Each element occupies a unique position on the periodic table based on its atomic number, which determines its electron configuration and chemical reactivity. For magnesium, its 12 protons set it apart as a distinctive element with its own unique characteristics.
In conclusion, determining the proton count of an element is a fundamental step in understanding its atomic structure and chemical properties. By grasping the concept of atomic number, we can unravel the mysteries of magnesium and appreciate its diverse roles in the natural world.
The Significance of Proton Count
Every element that makes up the world around us has a unique identity, and this identity is largely determined by the number of protons in its atomic nucleus. Protons are subatomic particles that carry a positive electric charge, and they play a crucial role in defining the properties of an element.
The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus is known as its atomic number, and it is this number that distinguishes one element from another. For instance, magnesium has an atomic number of 12, which means that every magnesium atom contains 12 protons in its nucleus. This number is what sets magnesium apart from all other elements, making it a unique substance with its own distinct set of characteristics.
The atomic number of an element is not just a random number; it is of utmost importance when it comes to identifying and classifying elements. In fact, the periodic table of elements is organized based on atomic number. By knowing the atomic number of an element, we can easily determine its position on the periodic table and gain valuable insights into its chemical behavior and properties.
So, the proton count in an atom is not just a number; it is a fundamental characteristic that defines the element’s identity and its place in the chemical world.